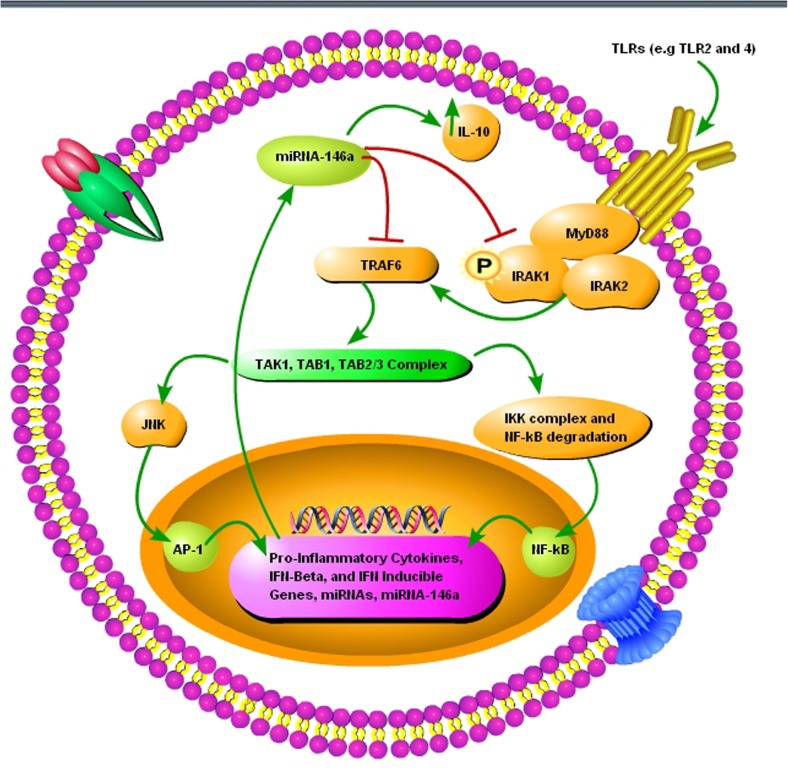
FIGURE 3.
A schematic diagram showing the importance of pro-inflammatory miRNA-146a during prion infection. (1) The toll-like receptors TRL2 and TLR4 are activated upon misfolded prion protein formation. (2) TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1), interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 2 (IRAK2), myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88) complexes are modulated in response to activated TLR2 and TLR4 receptors. (3) TRAF6 activates the c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) and IκB kinase (IKK) complex via TGF-beta activated kinase 1 (TAK1), TAK1-binding protein 1 (TAB1), and (TAB2/3) complex. (4) NF-κB degradation and nuclear translocation plus activator protein 1 (AP-1) activation via JNK result in upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines and several miRNAs including miRNA-146a. (5) Upregulated miRNA-146a inhibits IRAK1 and TRAF6 signaling to increase interleukin-10 (IL-10) secretion and reduce inflammation.