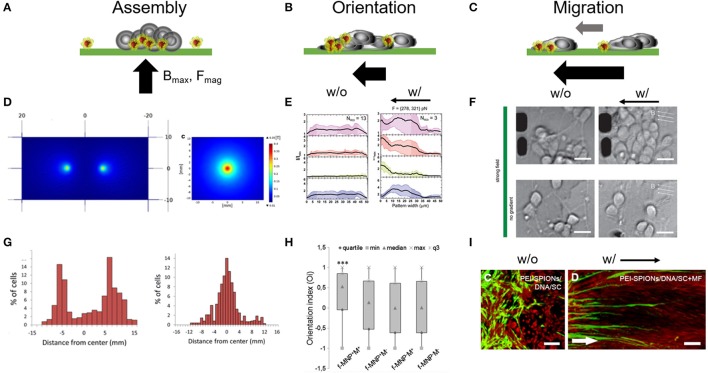
Figure 3.
Magnetic forces as cell patterning mediators. Tuning magnetic force amplitudes (Fmag), the position of the maximal magnetic field (Bmax) and the orientation of the magnetic field pole indicated through the black arrow provides a versatile approach for cell assembly. (A–C) Schematic represents different magnetic field gradient orientations and magnitudes and its impact on cell assembly and organization. (D) Single vs. two pole magnetic field gradient spots for positioning of cells. Reproduced with permission from Marcus et al. (2016), Copyright © 2016, BioMed Central. (E) Fluorescence distribution plots taken from primary cortical neuron cultures show a shift of intracellular markers toward left oriented magnetic gradient forces. w/o, no magnetic field; w/, with magnetic field. Reproduced with permission from Kunze et al. (2015). (F) Primary cortical neurons dissociated from rat brain tissues (E18) were cultured on poly-l-lysine surfaces and exposed to fMNPs after being 24 h in culture. These neurons grow and form neurite networks under magnetic fields and start migration toward magnetic field poles under strong magnetic forces (> 250 pN). Scale bar = 12 μm. Reproduced with permission from Kunze et al. (2015), Copyright © 2015, American Chemical Society. (G) Histogram plots of accumulated neuron-like cells which were cultured above the single and two pole patterns, respectively. (H) Orientation index extracted from PC12 that were observed to align in parallel to magnetic field orientation after being cultured with fMNPs. f-MNP-M+, fMNPs with magnetic field; f-MNP-M−, fMNPs without magnetic field. Reproduced with permission from Riggio et al. (2014), Copyright © 2014, Elsevier Inc. (I) Schwann cells migrate into astrocyte-rich region under an oriented magnetic field gradient after internalizing PEI-fMNPs (PEI-SPIONs). White arrow indicates direction of magnetic pole. Scale bar = 100 μm. Reproduced with permission from Xia et al. (2016), Copyright © 2016, Dove Medical Press Limited.