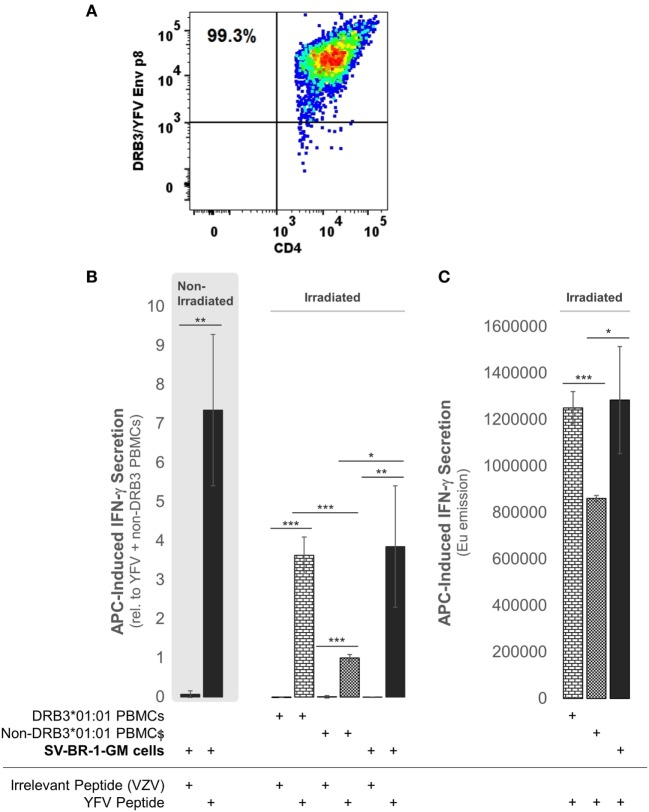
Figure 9.
SV-BR-1-GM cells act as antigen-presenting cells (APCs). SV-BR-1-GM cells were cultured and serum-starved for 24 h then coincubated with yellow fever virus (YFV) Envelope (Env) 43–59 peptides (35) known to bind to HLA-DR complexes with an HLA-DRB3*01:01-based β chain and a YFV-DRB3*01:01-specific CD4+ T cell clone (A). (A) T cell clone after staining with YFV Env p8/DRB3*01:01 tetramers, as assessed by flow cytometry. Almost all T cells are both YFV Env p8/DRB3 and CD4 positive. (B) After 72 h of coculturing, T cell activation was assessed by determining the levels of secreted interferon (IFN)-γ. Values shown are arithmetic means from technical triplicates ± SDs, normalized to the mean IFN-γ level obtained from the YFV peptide-treated non-DRB3 PBMC reference wells. Background IFN-γ levels obtained from T cells treated with peptides in the absence of APCs (SV-BR-1-GM or PBMCs) were subtracted. (C) IFN-γ levels without background subtraction and normalization of a part of the experiment represented by panel (B). Values shown are arithmetic means of the Europium emission values at 615 nm from technical triplicates ± SDs. (B,C) one-tailed Student’s t-tests were employed to assess significance, with * referring to 0.01 ≤ p < 0.05, ** to 0.001 ≤ p < 0.01, and *** to p < 0.001.