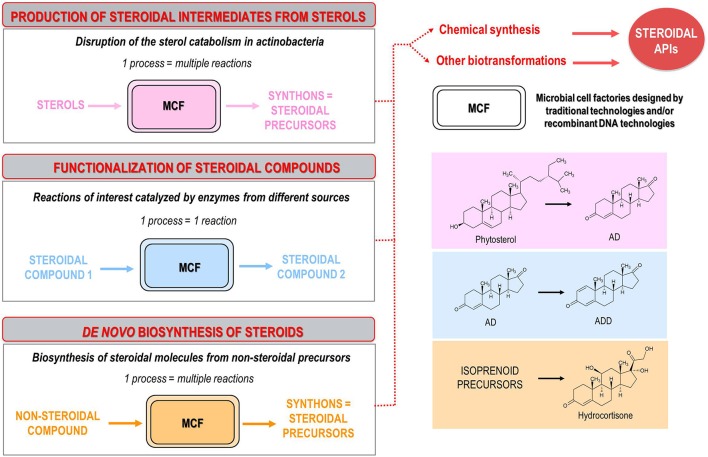
Figure 2.
Classification of the microbial bioprocesses for steroid synthesis described to date: (i) production of steroidal intermediates from natural sterols (e.g., bioconversion of phytosterols into ADD); (ii) functionalization of steroidal molecules (e.g., bioconversion of AD into ADD); (iii) de novo biosynthesis of steroids (e.g., biosynthesis of hydrocortisone from non-steroidal substrates). Several microbial strains, isolated from natural sources and improved by conventional mutagenesis or designed by using recombinant DNA technologies, are used as microbial cell factories (MCF) to produce key steroidal intermediates (synthons). The resulting synthons are subsequently modified by chemical steps or additional bioconversion processes to synthetize final steroidal active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).