FIGURE 10.
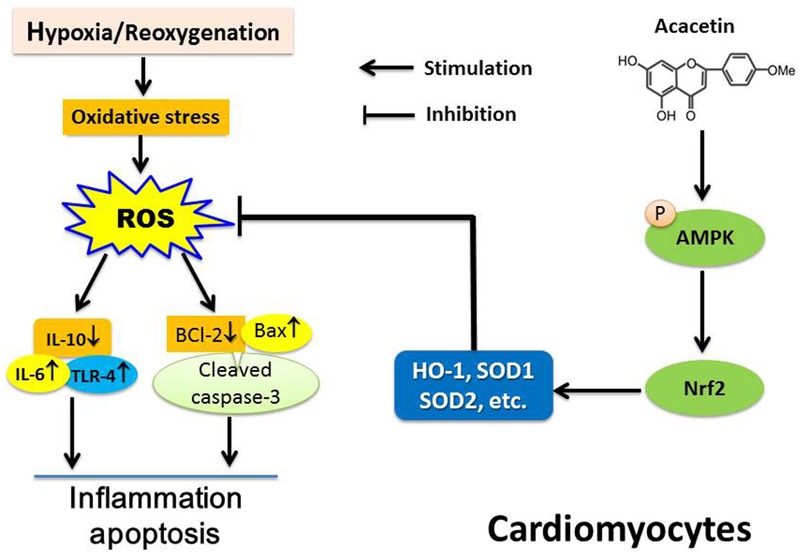
Schematic illustration showing the main cascade of molecules in cardiomyocytes subjected to ischemia/reperfusion insult and the mechanism of acacetin effects. Cardiomyocytes suffering from hypoxia/reoxygenation induces oxidative stress and triggers ROS production that induces inflammation and apoptosis via releasing the pro-inflammatory cytokines TLR-4 and IL-6 which increase the apoptotic proteins Bax and cleaved caspase-3, and decrease anti-inflammatory factor IL-10 and anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. Acacetin activates Nrf2 by stimulating AMPK, and increasing HO-1, SOD1, and SOD2, thereby conferring protection to cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation insult by reducing ROS production and inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis.
