Figure 7.
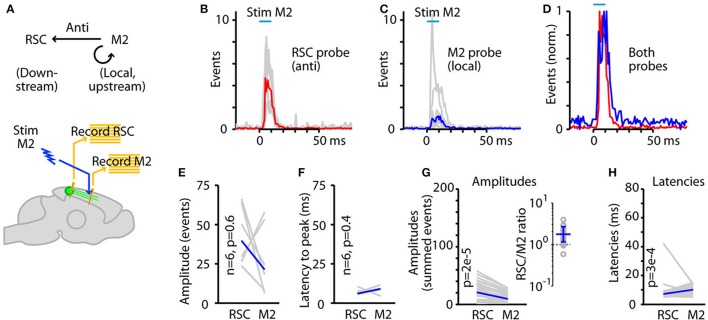
Driving in reverse: antidromic propagation. (A) Experimental paradigm: RSC neurons were infected with AAV to express ChR2, and photostimuli were applied to M2 (to stimulate axons of RSC neurons) while recording multi-unit activity in both M2 (locally driven) and RSC (antidromically driven).(B) Activity recorded on the RSC probe during RSC stimulation in an animal injected with AAV9-CaMKII-hChR2-eYFP. Red trace is the median response across animals (traces for each animal shown in gray). (C) Activity recorded on the M2 probe during the same experiment. Blue trace is the median response across animals. (D) Overall activity on the RSC and M2 probes plotted together (peak-normalized). (E) Amplitudes of responses (summed events) recorded on the RSC and M2 probes, for the same stimulus parameter combination (10-ms duration, 100% intensity) used for the data shown in (B-D), plotted for each experiment (gray) and as the median across animals (blue). P-value calculated by 2-sided, paired sign test. (F) Latencies (to peak) for responses recorded on the RSC and M2 probes (same stimulus). (G) Response amplitudes across all 25 stimulus parameter combinations (gray), with the overall median (blue), plotted for AAV9-CaMKII-hChR2-eYFP experiments (see text for AAV1-CAG-ChR2-Venus results). The RSC/M2 ratios for the 25 stimulus combinations are plotted on the right, with the geometric mean (error bars: geometric s.d.). (H) Same, for latencies.