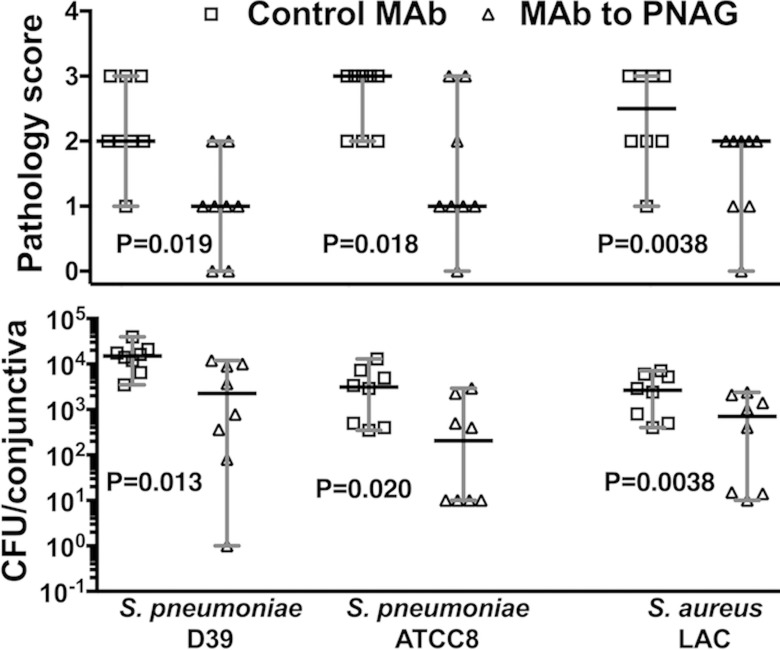
Figure 1.
Intraperitoneal administration of MAb to PNAG preinfection and postinfection reduces bacterial burdens and conjunctival pathology due to S. pneumoniae (D-39 and ATCC8) and S. aureus (LAC) after 48 hours of infection in A/J mice. Eighteen hours prior to infection and 4, 24, and 32 hours postinfection, 200 μg of the human IgG1 monoclonal antibody MAb F598 to PNAG or control IgG1 MAb F429 were injected IP. Mice (n = 8 per group) were euthanized at 48 hours postinfection and pathology scores (upper row) and CFU/conjunctiva (lower row) were determined. Symbols represent individual animals, black lines the median, and gray lines the 95% CI, and one-sided P values were determined by nonparametric t-tests.