Fig. 4.
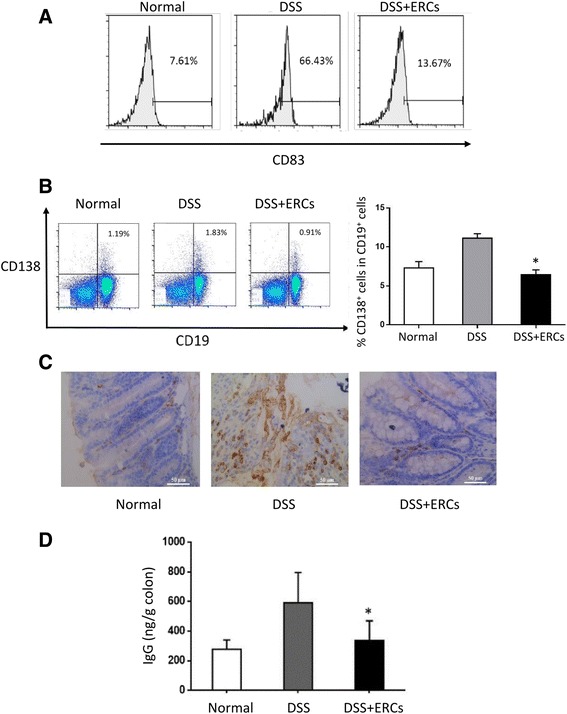
Endometrial regenerative cells (ERCs) inhibited B-cell activation, differentiation, and antibody deposition in colitis mice. The spleen was dissected and made into a single-cell suspension. Cells were stained with fluorescently labeled CD19, CD83, and CD138. a The expression of CD83 on CD19+ B cells and the proportion of b CD19+CD138+ cells in lymphocytes and CD138+ cells in CD19+ B cells was detected by flow cytometry. c IgG deposition in the colon. Colons were dissected and the distal part was paraffin sectioned with immunohistochemistry staining performed thereafter. Representative photographs of histological sections of colon from normal, untreated, and ERC-treated groups. Antibody deposition was observed by immunohistochemistry specific for IgG (×400). d The concentration of IgG in the colon was measured by ELISA. Graphs represent mean ± SEM of triplicate separate experiments. P value was determined by one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05. DSS, dextran sodium sulfate
