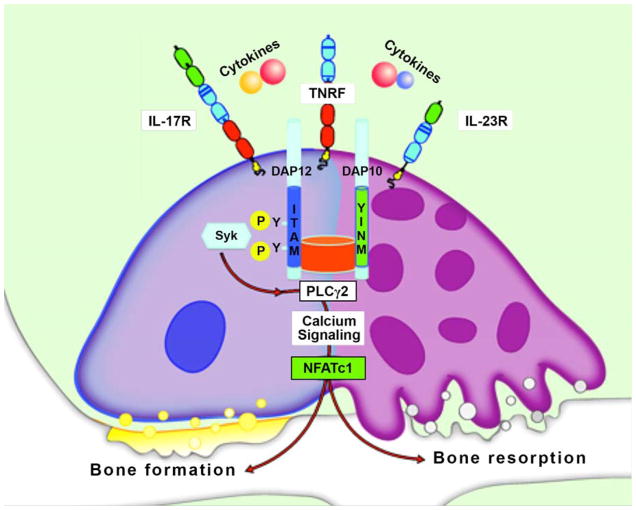
Figure 2. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of immune bone loss and bone formation.
Schematic representation of pro-inflammatory cytokine signaling showing activation of NFATc1 through calcium-dependent pathways. Although NFATc1 regulation of genes responsible for both bone loss and bone formation has been reported, certain immunoreceptors are restrictively expressed in myeloid cells. The possibility of cells of hematopoietic origin serving as osteogenic precursors at remote sites of tissue inflammation has also been proposed.