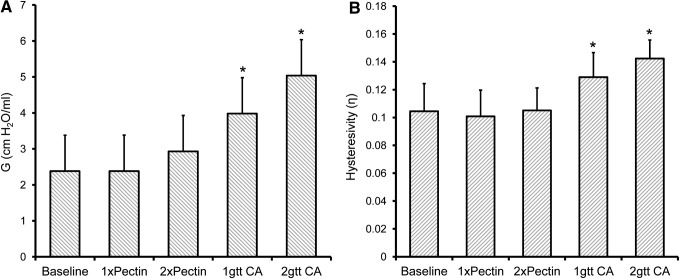
FIG. 5.
Effect of sealants on peripheral lung mechanics. Lung impedance measurements were made using a forced oscillation technique (FlexiVent). The no sealant condition (Baseline) was compared to two sizes of the pectin-based polymer (1xPectin, 25 mm2; 2xPectin, 50 mm2) as well as two volumes of a cyanoacrylate (CA, VetBond) sealant (1gtt, 25 μL; 2gtt, 50 μL). (A) Measurement of tissue damping (G) demonstrated a slight increase in the 2xPectin condition (p > 0.05), but a significant increase in both cyanoacrylate conditions (asterisk, p < 0.01). (B) Hysteresivity, reflecting the relationship between energy dissipation and energy conservation (elastance), demonstrated no difference in the pectin-based polymer conditions, but a significant increase in the cyanoacrylate treatment groups (asterisk, p < 0.01). Triplicate measures per mouse; each data point represents N = 3 mice.