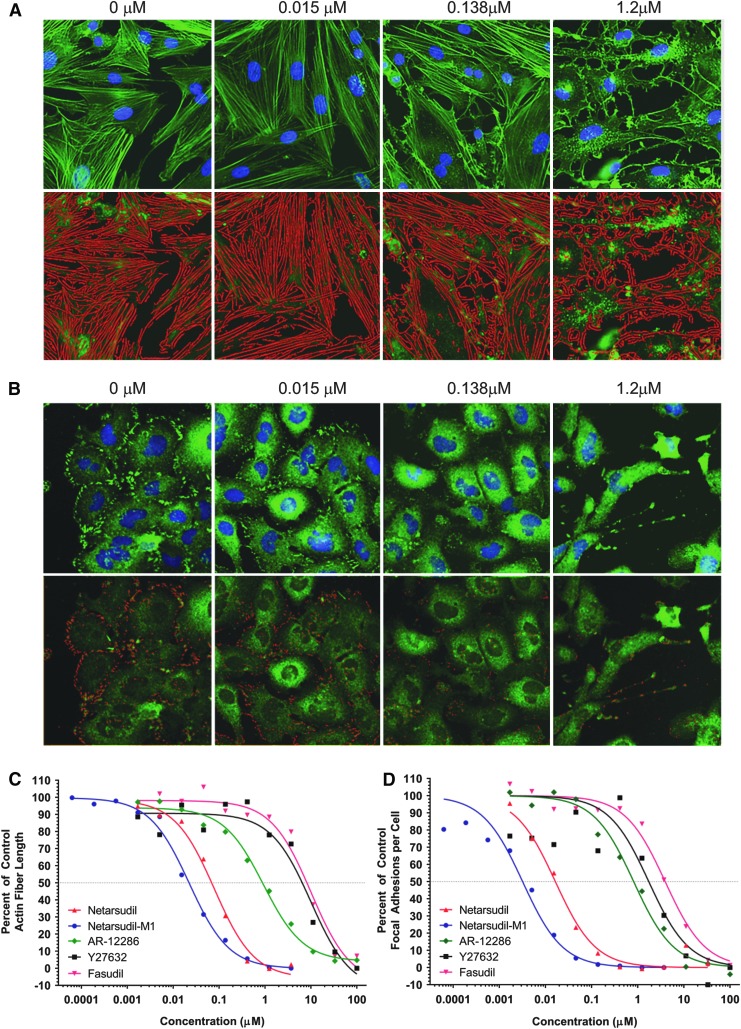
FIG. 2.
Disruption of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions by netarsudil versus other ROCK inhibitors. (A) Netarsudil dose-response in actin stress fiber assay. Primary PTM cells were incubated for 6 h in the presence of 0, 0.015, 0.138, or 1.2 μM netarsudil then fixed and stained with Alexa Fluor-488 phalloidin and Hoechst 33342 to reveal actin fibers and nuclei, respectively. Top panel: fluorescence images of stained cells. Bottom panel: False color images created by an automated, custom algorithm to identify stress fibers and calculate mean stress fiber length. (B) Netarsudil dose-response in focal adhesion assay. Immortalized HTM cells (TM-1) were incubated for 6 h in the presence of 0, 0.015, 0.138, or 1.2 μM netarsudil then fixed and stained with mouse anti-paxillin antibody/Alexa Fluor®488 goat-anti-mouse IgG and Hoechst 33342 to reveal focal adhesions and nuclei, respectively. Top panel: fluorescence images of stained cells. Bottom panel: False color images created by an automated, custom algorithm to identify focal adhesions and calculate the mean number of focal adhesions per cell. (C) Dose–response curves (n = 4) for netarsudil, netarsudil-M1, AR-12286, Y-27632, and fasudil in the PTM actin stress fiber length assay. Mean stress fiber length is presented as a percentage of the mean length of stress fibers measured in untreated control cells. (D) Dose–response curves (n = 4) for netarsudil, netarsudil-M1, AR-12286, Y-27632, and fasudil in the HTM focal adhesion assay. Mean number of focal adhesions per cell is presented as a percentage of the number of focal adhesions per cell measured in untreated control cells. HTM, human trabecular meshwork; PTM, porcine trabecular meshwork; ROCK, Rho-associated protein kinase.