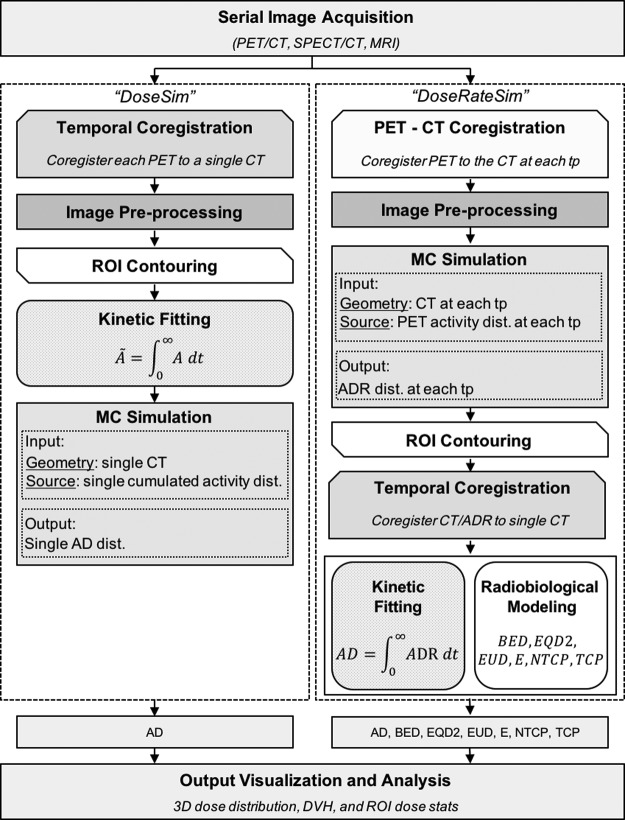
FIG. 1.
The RAPID framework and workflow. Serial 3D images (PET/CT or SPECT/CT) are acquired to map the agent's pharmacokinetics and geometry. The AD can be calculated using either the “DoseSim” or “DoseRateSim” method. In the “DoseSim” method, the activity distribution is time-integrated on a voxel-by-voxel basis to obtain a single cumulated activity distribution in the pharmacokinetic fitting module. A single CT and cumulated activity distribution are used as the input for the MC simulation that then generates a single absorbed dose distribution as output. In the “DoseRateSim” method, the PET/SPECT and CT at each TP are used as input for the Monte Carlo simulation and an ADR distribution is simulated for each time point. The absorbed dose rate at each time point is coregistered to a single CT and resampled. The absorbed dose is calculated by time-integrating the absorbed dose rate in kinetic fitting module and radiobiological dose metrics are calculated in the radiobiological modeling module. The dosimetry output includes 3D dose distributions, DVHs, DVH stats, and region of interest dose stats. 3D, three-dimensional; AD, absorbed dose; ADR, absorbed dose rate; DVHs, dose volume histograms; MC, Monte Carlo; RAPID, Radiopharmaceutical Assessment Platform for Internal Dosimetry; TP, time point.