Fig. 1.
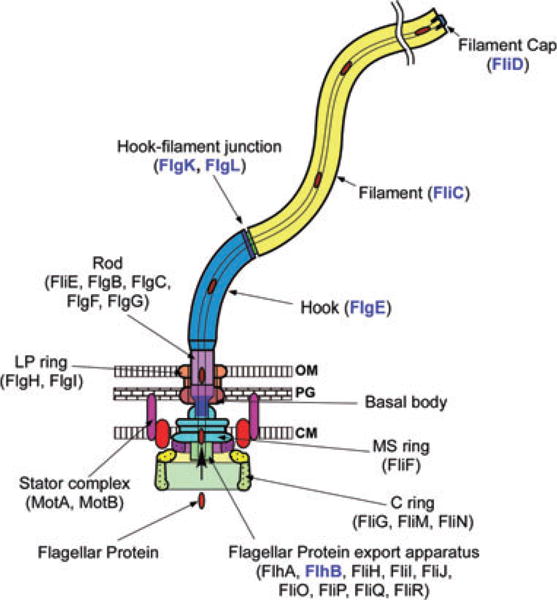
The bacterial flagellum can be roughly divided into three parts: the basal body, the hook and the filament. The different colours represent different protein components: FliF, MS ring protein; FliG, FliM and FliN, C ring component proteins; FlhA, FlhB, FliH, FliI, FliJ, FliO, FliP, FliQ and FliR, component proteins of the flagellar type III protein export apparatus; FliE, FlgB, FlgC, FlgF and FlgG, rod proteins; FlgH, Ling protein; FlgI, P ring protein; FlgE, hook protein; FlgK and FlgL, hook–filament junction proteins; FliC, filament protein (flagellin); FliD, filament-capping protein; MotA and MotB, the stator proteins. After the MS-C ring structure is assembled by FliF in the cytoplasmic membrane and FliG, FliM and FliN on the cytoplasmic surface of the FliF ring, flagellar component proteins are translocated into the central channel by the flagellar protein export apparatus, which is postulated to be located in a putative central pore of the MS ring. The rod assembly begins with FliE, FlgB, FlgC and FlgF followed by FlgG with the help of the rod cap made of the putative rod-capping protein FlgJ. Upon completion of the rod structure, the rod cap is presumably replaced by the hook cap, which is made of the hook-capping protein FlgD. After the rod is formed, FlgI and FlgH assemble around the rod in the peptidoglycan layer and outer membrane, respectively, to form the L–P ring complex. FlgE self-assembles into the hook at the tip of the distal rod with the aid of the hook cap. When the hook reaches its mature length, the ruler protein FliK interacts with FlhB, thereby allowing the export apparatus to switch its export specificity to substrates needed for the structure and assembly of the flagellar filament including the anti-sigma factor FlgM. The hook cap is replaced by FlgK, and then FlgL and FliD are bound at the distal end in this order. FliC then starts self-assembling into the long helical filament onto the hook–filament junction with the help of the filament cap made of FliD. FlgD, FlgJ, FliK and FlgM are not in the final structure of the flagellum. Location of RflH/Flk remains unknown but it is postulated to associate with the export apparatus. Component proteins relevant to this study are highlighted in blue.
