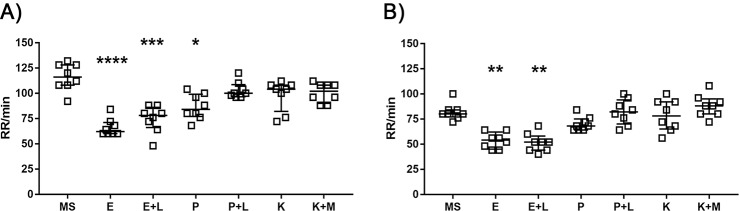
Fig 2. Respiratory rate (RR) per minute of adult zebrafish when treated with different anaesthetic protocols.
A) RR after loss of equilibrium and B) RR after loss of soft stimulus response of adult zebrafish after being subjected to an anaesthetic bath of: 100 μg/mL MS-222 (MS), 0.2 μg/mL etomidate (E); 0.2 μg/mL etomidate + 100 μg/mL lidocaine (E+L); 1.25 μg/mL propofol (P); 1.25 μg/mL propofol + 100 μg/mL lidocaine (P+L); 100 μg/mL ketamine (K); 100 μg/mL ketamine + 1.25 μg/mL medetomidine (K+M); or 100 μg/mL ketamine + 1.25 μg/mL medetomidine / 3.125 μg/mL atipamezole (K+M/A). Each point represents an animal (n = 8). Data are expressed as median [interquartile range]. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 when compared with MS-222. Non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test.