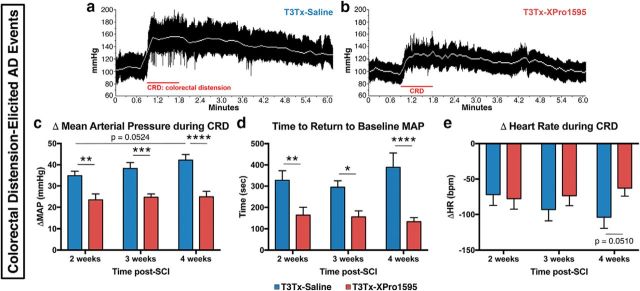
Figure 5.
XPro1595 treatment mitigates colorectal distension-induced AD. At 2, 3, and 4 weeks after T3Tx, HR and BP were determined in rats before, during, and after CRD, a well-established experimental means to elicit an AD episode that mimics constipation, a common trigger in SCI patients. a, b, Representative beat-to-beat arterial pressure traces from T3Tx-saline and T3Tx-XPro1595 animals 4 weeks after SCI. Red line indicates the 1 min CRD interval. White line indicates MAP. T3Tx-saline animals had stereotypical sharp spikes in MAP in response to CRD. T3Tx-XPro1595 animals exhibited a dramatically smaller increase in MAP. c, Quantification of the increase in MAP above baseline in response to CRD. The MAP increase in XPro1595-treated animals was significantly smaller than in saline-treated animals at every time point. Furthermore, there was a strong trend that the BP spike in the saline-treated animals progressively increased from 2 to 4 weeks (p = 0.054), further suggesting that AD worsens over time. Conversely, the MAP increase in the T3Tx-XPro1595 animals was stable at all 3 time points. d, The time that it took to return to baseline MAP after 1 min of CRD was significantly longer in T3Tx-saline animals than T3Tx-XPro1595 animals. e, We observed no significant differences in bradycardia (bpm; beats per minute) in response to CRD between groups, although there was a strong trend at 4 weeks (p = 0.051). Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 (two-way ANOVA and post hoc Fisher's LSD test). **p < 0.01 (two-way ANOVA and post hoc Fisher's LSD test). ***p < 0.001 (two-way ANOVA and post hoc Fisher's LSD test). ****p < 0.0001 (two-way ANOVA and post hoc Fisher's LSD test).