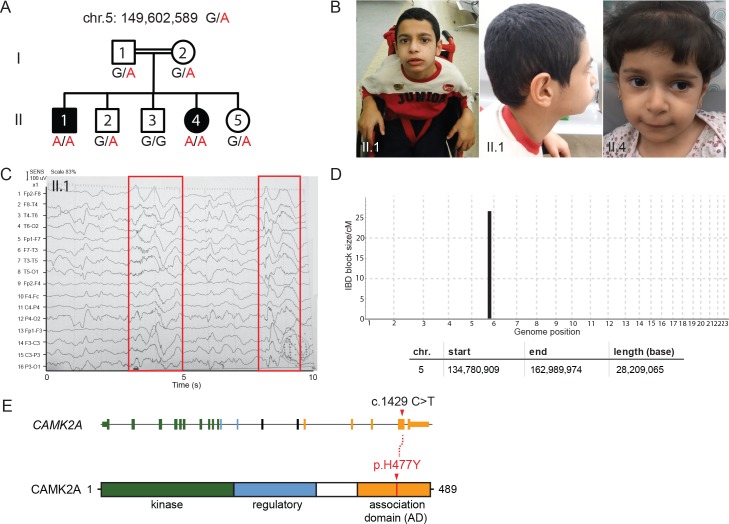
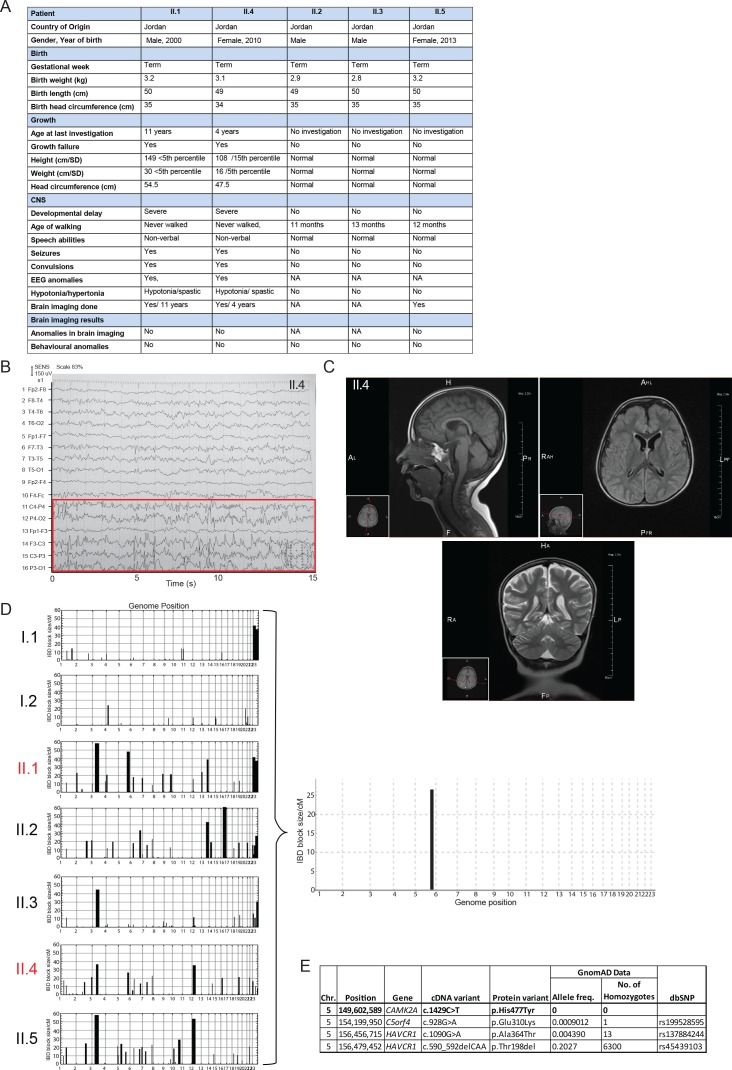
Figure 1. A new syndrome of global neuro-developmental delay with seizures caused by a biallelic mutation in CAMK2A.
(A) Pedigree of a consanguineous Jordanian family with two affected siblings with germline homozygous mutations in CAMK2A. The genotypes of all individuals were verified by Sanger sequencing. (B) Photographs of the two affected siblings with normal head circumferences. (C) EEG graph of patient II.I showing abnormal epileptiform transients (red boxes) (D) Homozygosity mapping delineates one candidate locus on chromosome 5. (E) CAMK2A exonic structure and CAMK2A protein domains. Patients II:1 and II:4 carry biallelic missense mutation p. H477Y located in CAMK2A association domain (AD). Nucleotide change c.1429 C > T refers to position on CAMK2A cDNA.