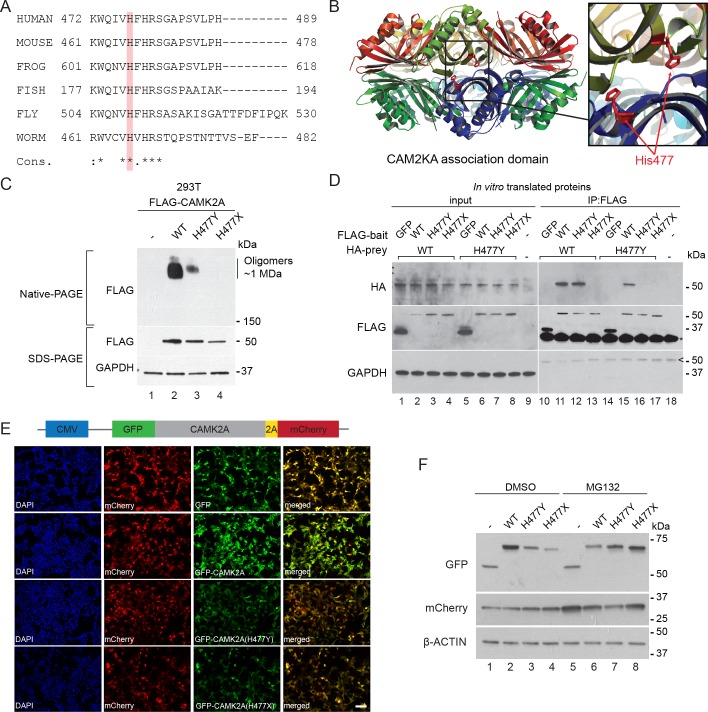
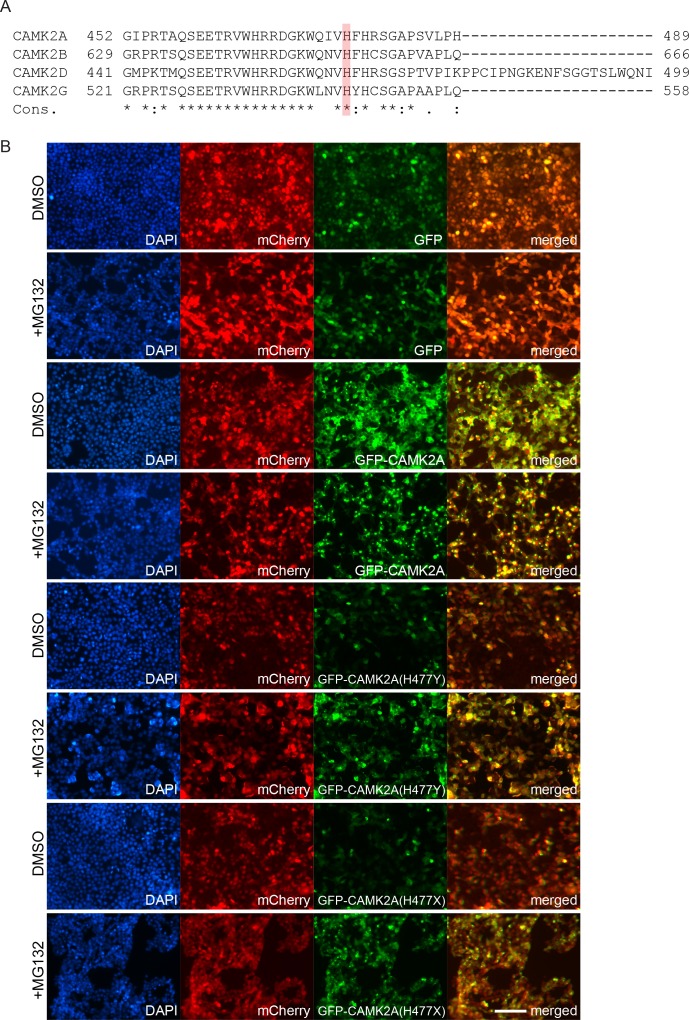
Figure 3. p.H477Y affects CAMK2A oligomerization and protein stability.
(A) Sequence conservation of CAMK2A homologs. Histidine 477 (H477) is highlighted in red. (B) X-ray crystal structure of human CAMK2A AD tetradecamer (PDB: 5IG3). H477 (red) is located at the equatorial dimer interface. (C) Defective oligomerization of the p.H477Y mutant. 293 T cells were transiently transfected with FLAG tagged wild-type CAMK2A and CAMK2AH477Y. A third mutant, CAMK2AH477X which lacks part of the AD (a.a. 478–489) was used as positive control. (D) Defective self-association of the p.H477Y mutant. The indicated FLAG- and HA-tagged CAMK2A wild-type and mutant proteins were synthesized in vitro using rabbit reticulocyte lysate. FLAG-GFP was used a negative control. FLAG-tagged proteins were immunoprecipitated using anti-FLAG M2 agarose resin in the presence of 1% NP40. Co-immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. *, IgG light chain. ^, IgG heavy chain. (E) p.H477Y mutation lowers expression of CAMK2A in cells. 293 T cells were transfected with reporter plasmids encoding GFP-tagged wild-type CAMK2A, CAMK2AH477Y and CAMK2AH477X mutants, followed by T2A peptide and mCherry. Representative confocal images show lower expression of mutant GFP- CAMK2AH477Y compared to wild-type. Scale bar represents 100 µm. (F). p.H477Y decreases CAMK2A stability via proteasomal degradation. 293 T cells were transfected as in (E) and treated with 10 µM MG132 or DMSO for 16 hr. 10 µg total cell lysate was used for SDS-PAGE and Western blot.