Figure 4. SARM1 deficiency protects RGCs from axon degeneration after ONC.
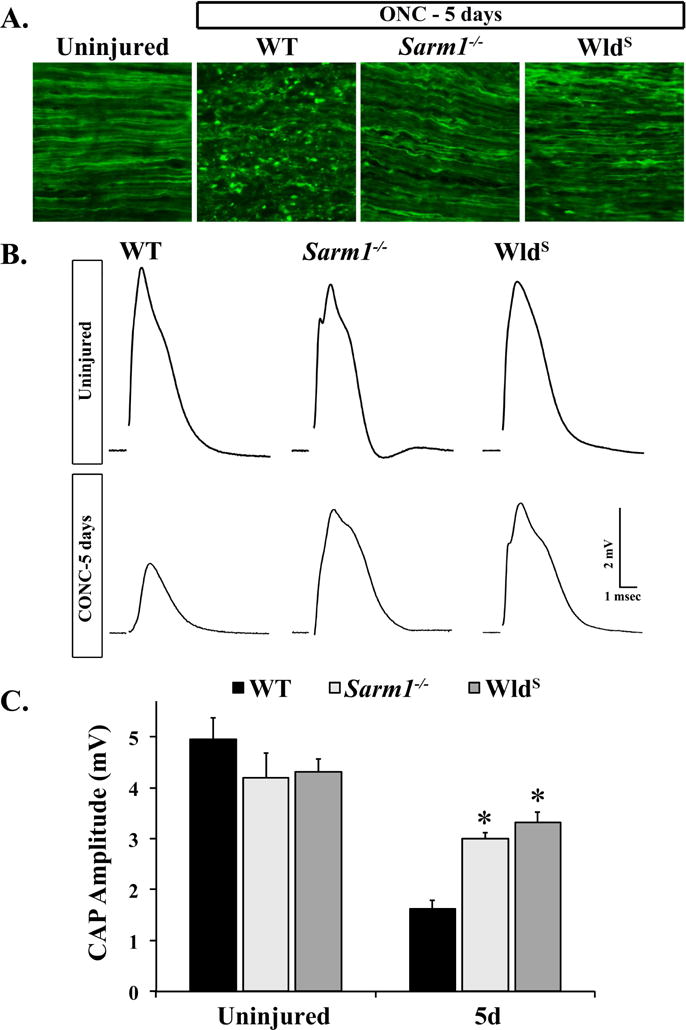
A. Representative images of longitudinal optic nerve sections from mice of the indicated genotypes in which RGC axons were labeled with CFP by crossing the Thy-CFP transgene into the strain (CFP+). Histological signs of axon degeneration such as axon beading and fragmentation were evident in WT optic nerves 5 days after ONC. However, fewer morphological signs of axon degeneration were observed in Sarm1−/−.CFP+ and WldS.CFP+ optic nerves 5 days after ONC (n = 3 for each genotype). B. Representative traces of the CAP recorded from WT, Sarm1−/− and WldS optic nerves 5 days after crush. C. SARM1 deficiency significantly reduced RGC axon degeneration 5 days after crush. The CAP amplitude recorded from Sarm1−/− and WldS nerves was significantly higher than WT nerves 5 days after ONC. Interestingly, the CAP amplitude was not significantly different in Sarm1−/− and WldS nerves 5 days after ONC (n ≥ 5 for each genotype and condition; error bars, SEM). Note, Sarm1+/+ and WldS littermate controls that did not carry the mutation were grouped together in the WT group.
