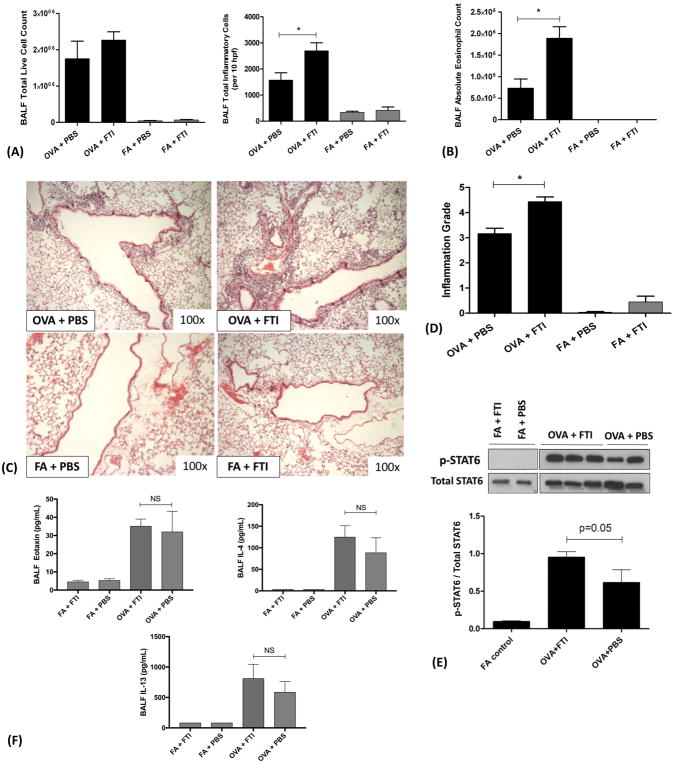
Figure 4. FTase Inhibition with FTI-277 Exacerbates Allergic Airway Inflammation in a IL4/IL13/STAT6/eotaxin-Independent Manner.
BALB/c mice were sensitized to ovalbumin (OVA) and then challenged with 1% OVA aerosol or filtered air six times over a 2-week period. Mice were injected daily with FTI-277 (20 mg/kg/day, i.p.) before each OVA aerosol exposure. To assess for inflammation and drug effect, we quantified total and differential inflammatory cell counts and chemokines/cytokines in BALF, assessed histopathology and Inflammation Grade by H&E staining, and measured total- and phosphorylated STAT6 in whole lung homogenate by Western blot.
(A) In OVA-exposed mice, treatment with FTI-277 did not significantly increase BALF total live cell count (p=NS by 1-way ANOVA). However, measured as BALF total inflammatory cells/per 10 hpf, FTI-277 treatment of OVA-exposed mice increased inflammatory cell influx by 1.72-fold with (*p<0.05, by 1-way ANOVA). Treatment with FTI-277 had no detectible pro-inflammatory effects in any of the FA control groups.
(B) Treatment with FTI-277 increased BALF absolute eosinophil count by 2.58-fold, (OVA+PBS vs. OVA+FTI, *p<0.01 by 1-way ANOVA).
(C) H&E stained lung sections indicate that treatment with FTI-277 augmented peribronchial and perivascular inflammation in the OVA-exposed mice.
(D) Semi-quantification of the H&E sections corresponded to a 1.40-fold increase in the Inflammation Grade (*p<0.001, by 1-way ANOVA). There were no statistically significant effects of FTI-277 on Inflammation Grade in the FA-exposed control groups.
(E) In OVA-exposed mice, there was a significant increase in STAT6 phosphorylation as compared to FA controls. Treatment with FTI-277 further increased OVA-induced STAT6 phosphorylation by 1.55-fold, but this was not statistically significant (OVA+PBS vs. OVA+FTI, p=0.05, by 1-way ANOVA).
(F) Cytokines IL4 and IL13 induce phosphorylation of the transcription factor STAT6 which then activates the transcription of eotaxin. To assess this, we measured peptide levels of secreted IL4, IL13, and eotaxin in BALF. There were no statistically significant differences in BALF eotaxin levels (p=NS, by 1-way ANOVA) with FTI-277 treatment in either FA or OVA groups. The cytokine IL-4 was significantly induced in BALF upon OVA exposure (OVA+FTI vs. FA+FTI, p=0.0371 by 1-way ANOVA), however, there were no statistically significant differences in BALF IL-4 levels with FTI-277 treatment in either FA or OVA groups (p=NS, by 1-way ANOVA). There were no statistically significant differences in BALF IL-13 levels with FTI-277 treatment in either FA or OVA groups (p=NS, by 1-way ANOVA).