Figure 2. Inhibition of the Arp2/3 complex and its activators WAVE and N-WASP-VCA by the ACD-cross-linked actin oligomers.
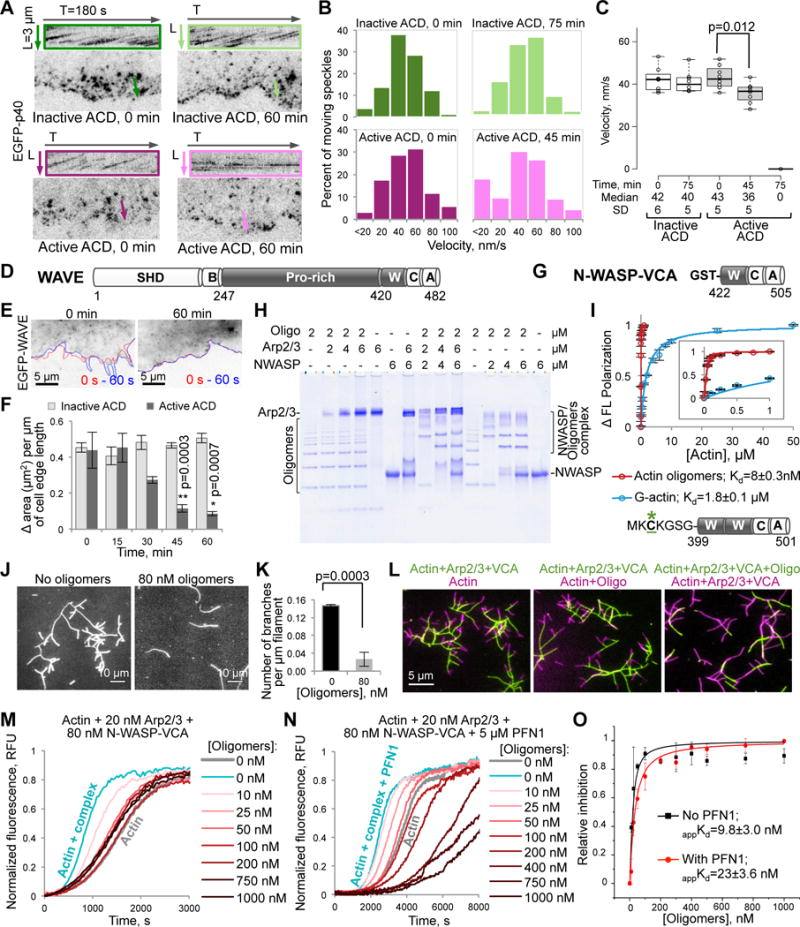
(A–C) Movement of individual speckles of EGFP-p40 subunit of the Arp2/3 complex in XTC cells represented as (A) kymographs (colored boxes), (B) distributions of moving p40 speckles’ velocities (100–300 displacement events), and (C) a box plot of velocities calculated from individual speckle tracks (n=8; median velocities and SD are indicated). See also Movie S2.
(D) Domain structure of X. laevis WAVE: SHD, SCAR-homology domain; B, basic region; Pro-rich, proline-rich region; W, WH2-domain; C, central domain; A, acidic motif. Residue numbers delineating domain borders are indicated.
(E,F) The cell edge dynamics of EGFP-WAVE-transfected XTC cells is illustrated by changes of the cell contour (E) in two images taken within 60 seconds from each other (red line – at 0 s, blue – at 60 s). (F) Quantitation of the cell edge dynamics represented as an area change per micrometer of the cell edge length (data is mean ± SE; n=4). See also Movie S3.
(G) Domain organization of GST-N-WASP-VCA used in native PAGE (H), TIRFM (J–L), and pyrene assays (M–O) – the C-terminal part (a.a. 422–505) of bovine N-WASP: W, WH2-domain; C and A, central and acidic domains, respectively.
(H) A representative native PAGE (n=3) of the oligomers titrated by the Arp2/3 complex, GST-N-WASP-VCA, and their combination.
(I) Fluorescein-labeled (green asterisk) murine N-WASP-VCA (a.a. 399-501) with two WH2-domains and without GST-tag (50 nM) was used in fluorescence polarization assays to calculate the Kds of N-WASP-VCA to actin monomers and actin oligomers (data is mean ± SD; n=3). Insert is a blow-up view of 0 to 1 μM [Actin] range.
(J,K) Branching events formed upon mixing of Alexa 488-actin with the Arp2/3 complex (20 nM) and GST-N-WASP-VCA (40 nM) in the presence or absence of oligomers in TIRFM (J), were quantified and normalized to the total filament lengths (K); mean ± SD; n=3. See also Movie S4.
(L) Two-color TIRFM (left and middle panels) demonstrates that existing branches formed in the presence of Arp2/3-N-WASP-VCA (green filaments) do not dissociate and continue to elongate after the addition of oligomers and a concomitant removal of Arp2/3-N-WASP complexes (magenta filaments). Oligomers block branch formation (right panel; green filaments), which is restored upon removal of the oligomers (magenta filaments).
(M–O) Effects of the oligomers on the GST-N-WASP-VCA-activated Arp2/3-mediated actin nucleation in bulk pyrenyl-actin assays in the absence (M; see also Figure S1A) and presence (N) of PFN1; relative inhibition data in (O; see STAR Methods) presented as mean ± SD, n=3.
