Figure 4. Inhibitory effects of actin oligomers on Ena/VASP-mediated processive filament elongation.
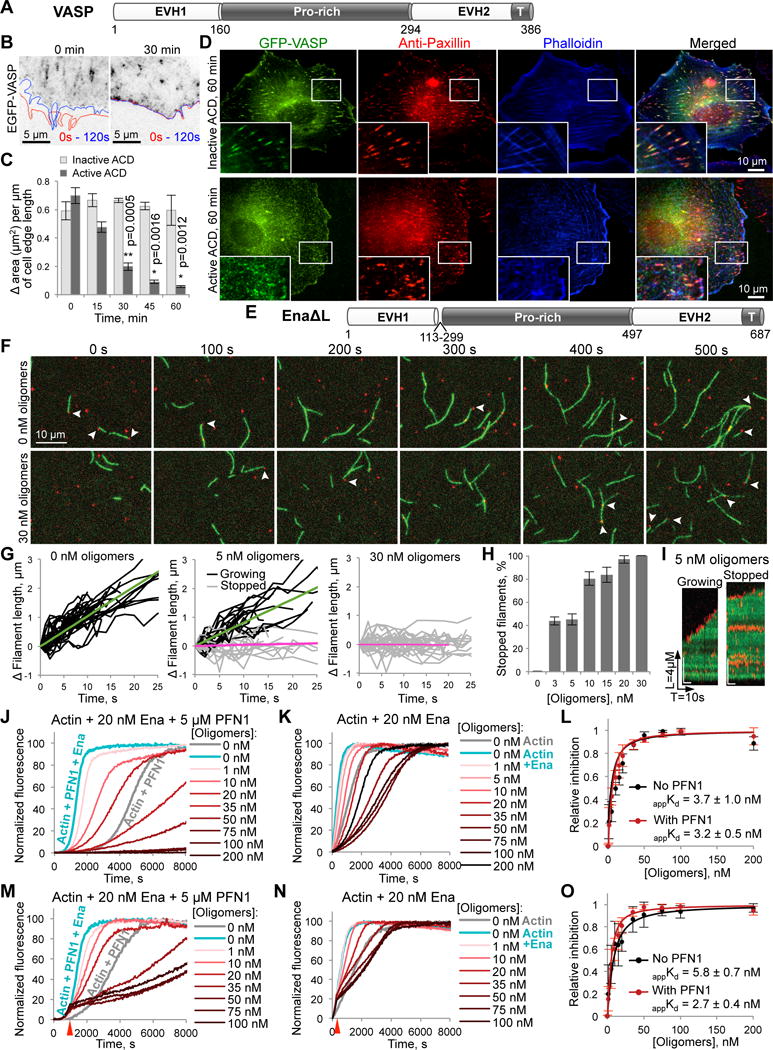
(A) Domain structure of X. laevis VASP protein: EVH1 and EVH2, Ena/VASP-homology domains 1 and 2; Pro-rich, (poly)proline-rich domain. EVH2 contains a putative WH2-domain and a tetramerization domain (T).
(B,C) The leading edge dynamics in EGFP-VASP-transfected XTC cells is illustrated by changes of the cell contour (B) in two images taken within 2 min from each other (red line – at 0 s, blue – at 120 s). The dynamics was stalled within 30 min upon delivery of active ACD as demonstrated by virtually overlapping cell contours. (C) Quantitation of the cell edge dynamics represented as an area change per micrometer of the cell edge length (data is mean ± SE; n=4). See also Movie S6.
(D) XTC cells expressing high levels of EGFP-VASP were treated for 60 min with either active or inactive ACD, stained for paxillin (red), and counterstained with phalloidin (blue). “Blow-up” images of boxed areas are shown in the lower left corners.
(E) Domain organization of EnaΔL construct corresponding to fly Ena lacking a linker region (a.a. 113-299); domain designation as in (A).
(F–I) Single-molecule TIRFM time-lapse images (F) of Alexa 488-actin (green) polymerization in the presence of 0.5 nM SNAP-EnaΔL (red), 3 µM chickadee, and either no oligomers or 30 nM oligomers. Arrows indicate SNAP-EnaΔL-bound barbed ends. (G) Filament elongation traces of SNAP-EnaΔL-bound filaments with 0, 5, and 30 nM oligomers. Fit lines show average growth rates of SNAP-EnaΔL-bound growing filaments (green fits) and SNAP-EnaΔL-bound stopped filaments (magenta fits). (H) The percent of SNAP-EnaΔL-bound stopped filaments was determined over a range of actin oligomer concentrations and expressed as mean ± SD, n=3. (I) Kymographs of growing and stopped SNAP-EnaΔL-bound filaments in the presence of 5 nM of actin oligomers. See also Movie S7.
(J–O) Effects of actin oligomers on Ena-mediated actin polymerization in the presence (J,M) or absence of PFN1 (K,N) with oligomers added at the start of polymerization (J,K) or at the time point when ~15% of actin was polymerized (M,N; red arrows). (L,O) Inhibition of Ena-controlled actin polymerization as determined from triplicates of (J,K) and (M,N), respectively; data is mean ± SD (see STAR Methods). See also Figure S1B.
