Figure 5. Inhibition of Spire-mediated actin nucleation by the actin oligomers.
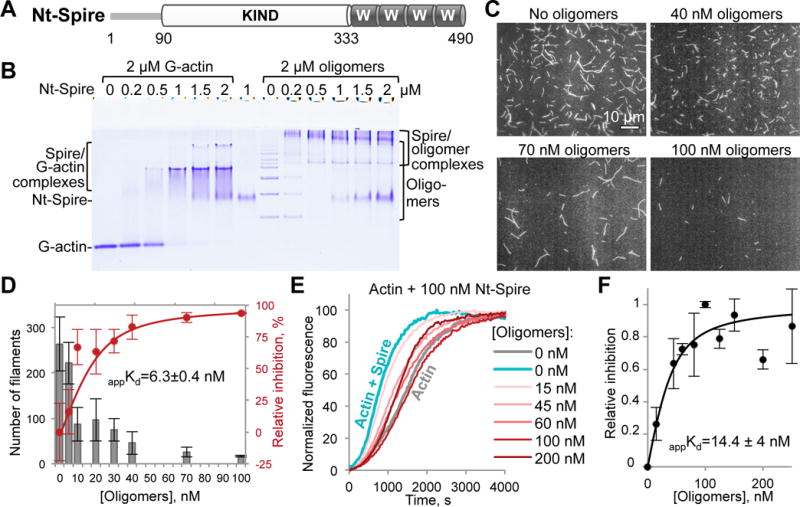
(A) Domain organization of the Nt-Spire construct corresponding to the N-terminal part (a.a. 1-490) of drosophila Spire: KIND, kinase non-catalytic c-lobe domain, W, WH-2-domain.
(B) A representative native gel (n=3) of G-actin and ACD-cross-linked actin oligomers titrated by Nt-Spire. Formation of complexes is indicated by the appearance of bands of lower electrophoretic mobility as compared to the individual protein bands.
(C,D) Single-color TIRFM images (C) taken at 8 min of polymerization of Alexa 488-actin in the presence of 20 nM Nt-Spire and various concentrations of the oligomers, as indicated. (D) Number of actin filaments formed in (C) was quantified from three independent experiments, expressed as mean ± SE (grey bars), and used to generate a relative inhibition curve (red) and obtain an apparent Kd (appKd) as described in STAR Methods.
(E,F) Nucleation of pyrene-actin by Nt-Spire was inhibited by the indicated concentrations of the oligomers in bulk actin polymerization assay (E; see also Figure S1C). Inhibition of the Spire-mediated actin nucleation by the oligomers (F) was assessed from three independent experiments, expressed as mean values ± SD, and the apparent Kd value (appKd) was calculated as described in STAR Methods.
See also Movie S8.
