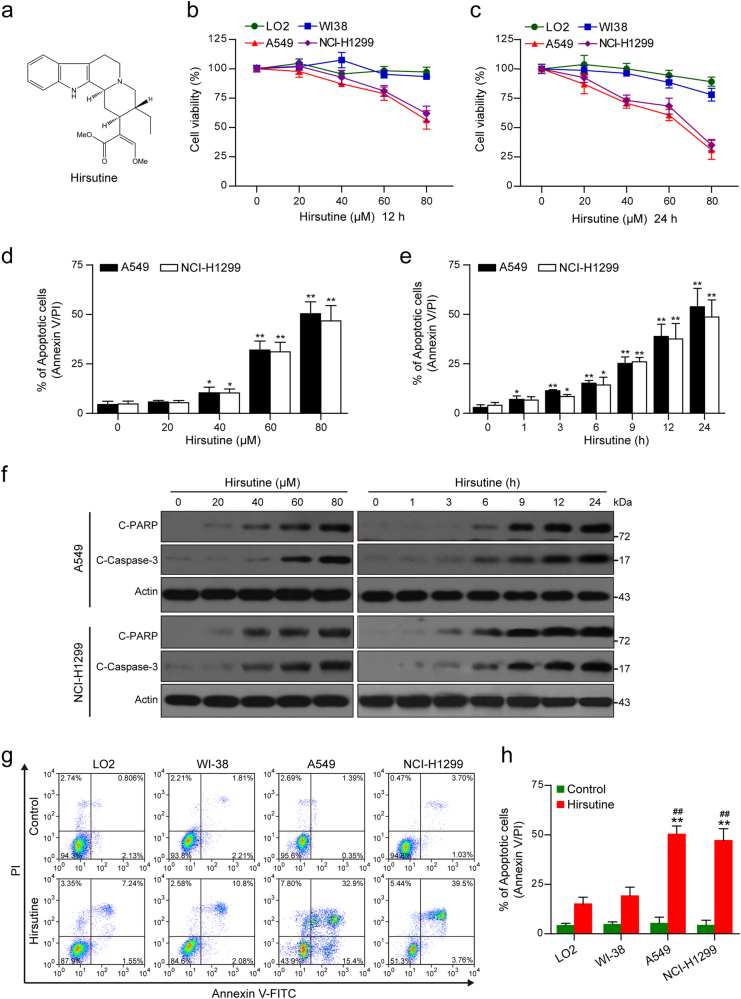
Fig. 1. Hirsutine selectively inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human lung cancer cells.
a The chemical structure of hirsutine. b, c Human normal hepatocyte LO2 cells, human lung epithelial fibroblast WI38 cells, and human lung carcinoma A549 and NCI-H1299 cells were treated with various concentrations of hirsutine for 12 or 24 h; cell viabilities were determined by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). d, e A549 and NCI-H1299 cells were treated with various concentrations of hirsutine for 24 h or 80 μM hirsutine for different time intervals. The percentage of apoptotic cells was determined by flow cytometry using Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. the control group. f Whole-cell lysates were prepared and subjected to western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies against cleaved-PARP (C-PARP), cleaved-caspase 3 (C-Caspase 3). g, h LO2, WI38, A549, and NCI-H1299 cells were treated with 80 μM hirsutine for 24 h, followed by staining with Annexin V-FITC/PI and analyzed by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3), **P < 0.01 vs. LO2 cells treated with hirsutine, ##P < 0.01 vs. WI-38 cells treated with hirsutine