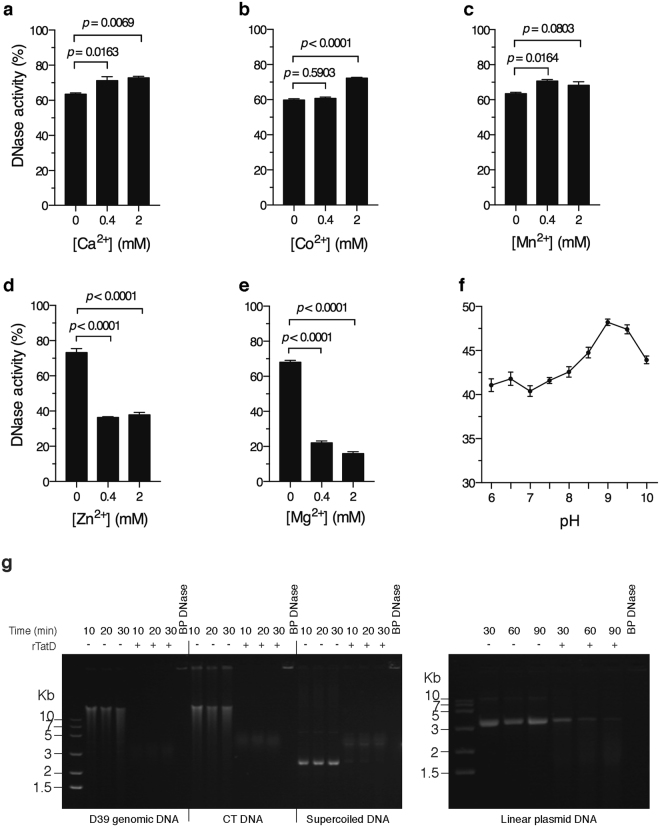
Figure 4.
Biochemical characterization of rTatD. (a–e) Analysis of the effect of presence or absence of various divalent cations on DNase activity of rTatD by picogreen assay. The reaction was performed in 40 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.7) in the absence or presence of 0.4 or 2 mM Ca2+ (a), Co2+ (b), Mn2+ (c), Zn2+ (d) or Mg2+ (e). The DNase activity is represented as mean ± sem of triplicates. The experiment was done twice and data from a representative experiment is shown. One-way ANOVA (with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test) was used for statistical analysis of data presented in panels a-e. (f) Effect of pH on DNase activity of rTatD. The reaction was performed in the same reaction buffer as used in DNase assay but with the pH ranging from 6 to 10. The DNase activity was estimated using picogreen assay. Error bars represent mean ± sem of triplicates. A representative of three independent experiments is presented. (g) The ability of rTatD to digest DNA substrates of different topologies was checked at the indicated time points. Genomic DNA from pneumococcal strain D39, calf thymus DNA (CT DNA), supercoiled or linearized double-stranded plasmid DNA was incubated with 10 μM rTatD for the indicated time duration. The samples were resolved on an agarose gel containing ethidium bromide. Bovine pancreatic DNase I (BP DNase) was used as the positive control. A representative of three independent experiments is shown. The full-length gels are presented in Supplementary Fig. S7.