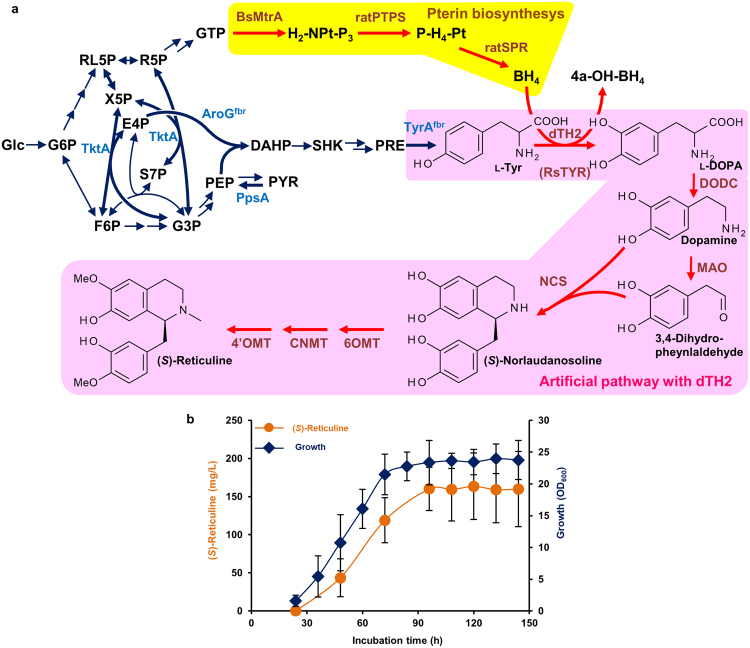
Figure 1.
Alternative platform for benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA) biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. (a) Biosynthetic platform for BIAs in E. coli. Bold arrows indicate the modified reactions. The colour codes are as follows: blue, inherent enzymes; red, heterologous enzymes. The pink- and yellow-shaded zones indicate the artificial pathway for BIA synthesis and for de novo BH4 synthesis, respectively. Abbreviations of the compounds and enzymes are as follows: G6P, d-glucose 6-phosphate; F6P, d-fructose 6-phosphate; RL5P, d-ribulose 5-phosphate; R5P, d-ribose 5-phosphate; X5P, d-xylose 5-phosphate; E4P, d-erythrose 4-phosphate; S7P, d-sedoheptulose 7-phosphate; G3P, d-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PYR, pyruvate; DAHP, 3-deoxy-d-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate; SHK, shikimate; PRE, prephenate; H2-NPt-P3, 7,8-dihydroneopterin triphosphate; P-H4-Pt, 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; 4a-H-BH4, 4a-hydroxytetrahydrobiopterin; TyrAfbr, chorismate mutase-prephenate dehydrogenase (feedback-resistant); AroGfbr, 2-dehydro-3-deoxyphosphoheptonate aldolase; TktA, transketolase; PpsA, phosphoenolpyruvate synthetase; dTH2, tyrosine hydroxylase; RsTYR, tyrosinase; DODC, l-DOPA decarboxylase; MAO, monoamine oxidase; 6OMT, norcoclaurine 6-O-methyltransferase; 4′OMT, 3′-hydroxy-N-methyl-(S)-coclaurine 4′-O-methyltransferase; CNMT, coclaurine N-methyltransferase; BsMtrA, GTP cyclohydrolases I; ratPTPS, 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase; and ratSPR, sepiapterin reductase. (b) Fermentative production of (S)-reticuline with strain EM353 in a jar fermenter. (S)-Reticuline was obtained from seven independent experiments; in three experiments, production was analysed at 24–96 h and in four experiments at 72–144 h. Error bars represent SD.