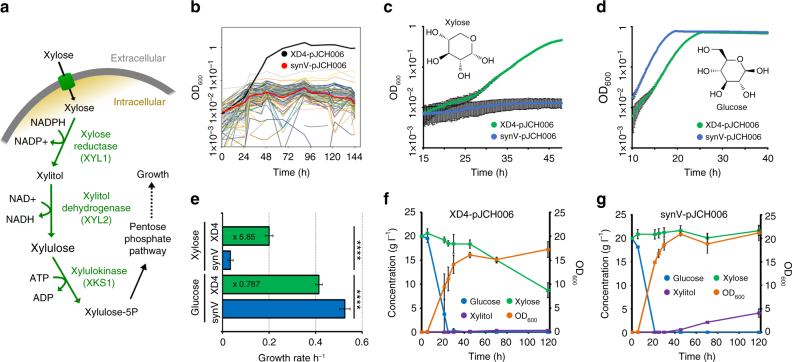
Fig. 2.
SCRaMbLE generates a host strain specialised for xylose utilisation. a Xylose oxidoreductase pathway through which xylose is converted to xylulose-5 phosphate before entering the pentose phosphate pathway. Enzymes with names in green are encoded by genes on pJCH006. b OD600 values for the initial 96-well based screening of colonies in SCX URA− medium. The synV-pJCH006 control and the colony in well D4 are highlighted, n = 1. c The growth of XD4-pJCH006 and synV-pJCH006 in synthetic xylose medium over 48 h in 96-well format, n = 19. d The growth of XD4-pJCH006 and synV-pJCH006 in synthetic glucose medium over 48 h in 96-well format, n ≥ 18. e The growth rate per hour of XD4-pJCH006 and synV-pJCH006 in synthetic xylose and synthetic glucose media in 96-well format. Rates were calculated over 5 h of exponential growth, n ≥ 18. f HPLC-derived concentrations of glucose, xylose and xylitol and the optical density (OD600) of 25 ml XD4-pJCH006 cultures in SC URA− medium with 2% glucose and 2% xylose over time, n = 2. g The equivalent data derived from synV-pJCH006 cultures, n = 2. All values plotted are mean averages and error bars represent 1 standard deviation from the mean. Replicate numbers represent biological replicates. Asterisks denote two-tail p-value as determined by two-sample t-test, with ****p ≤ 0.0001