Table 1.
Selected medications of different classes that are currently used to manage different ASD symptoms.
| Class | Medication | Structure | Pharmacological effects | Side effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atypical Antipsychotics | Clozapine | 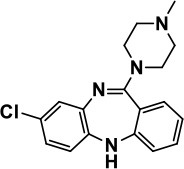 |
Improves hyperactivity and aggression in ASD patients | Requires patient's hematological safety monitoring and it lowers seizure threshold | Zuddas et al., 1996; Chen et al., 2001; Gobbi and Pulvirenti, 2001; Sahoo et al., 2017 |
| Risperidone | 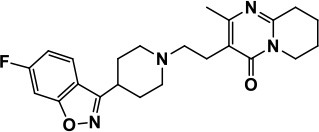 |
Reduces irritability, repetitive behavior, aggression, anxiety, and depression & nervousness. It shows neuroprotective activity, modulates astroglia function, and increases the brain antioxidant activity. | Mild sedation, increased appetite, fatigue, dizziness, drowsiness, tremor, and constipation | McDougle et al., 1998b; McCracken et al., 2002; Hara et al., 2017 | |
| Aripiprazole |  |
Reduces autistic symptoms in children such as irritability, stereotypy, and hyperactivity | Fatigue, vomiting, weight gain, tremor, and extrapyramidal symptoms | Marcus et al., 2009; Owen et al., 2009; Hirsch and Pringsheim, 2016 | |
| Selective Serotonin Reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) | Fluoxetine |  |
Reduces stereotyped and repetitive behavior in children and adolescents with ASD. | Hypomania. agitation, and hyperactivity | Fatemi et al., 1998; DeLong et al., 2002; Hollander et al., 2005; Hendriksen et al., 2016 |
| Fluvoxamine | 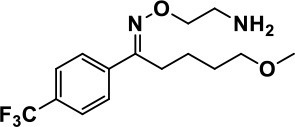 |
Improves compulsive repetitive behaviors, aggression | Irritability, and increase risk of suicidal ideas | McDougle et al., 1996; Martin et al., 2003; Brown et al., 2017; Howes et al., 2018; Lee et al., 2018 | |
| Sertraline | 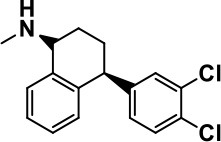 |
All SSRIs possess similar effects to fluoxetine and fluvoxamine. Sertraline shows improvements in repetitive and disruptive behavior in adults with ASD, paroxetine reduced aggression, and escitalopram shows improvements in irritability, stereotypy, hyperactivity and inappropriate speech. | Hellings et al., 1996; McDougle et al., 1998a; AlOlaby et al., 2017 | ||
| Paroxetine | 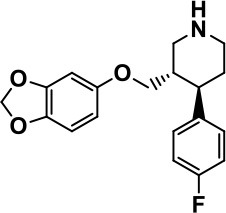 |
Davanzo et al., 1998; Hellings et al., 2015 | |||
| Escitalopram | 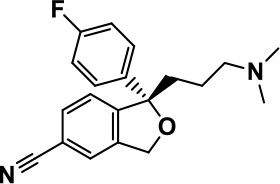 |
Owley et al., 2005; Brown et al., 2017; Viktorin et al., 2017 | |||
| Venlafaxine | 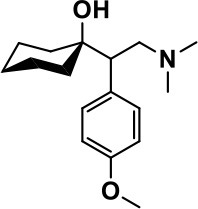 |
Improves restricted behavior and interest, social and communication deficits, and hyperactivity | Irritability, and increase risk of suicidal idea | Carminati et al., 2006, 2016 | |
| Tricyclic Antidepressant | Nortriptyline | 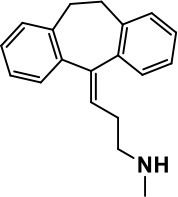 |
Improves hyperactivity and aggressiveness in autistic children | Sedation, increase in aggression, irritability and hyperactivity | Kurtis, 1966; Campbell et al., 1971; Hong et al., 2017 |
| Clomipramine | 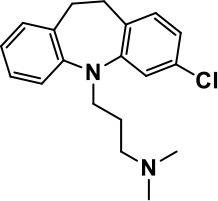 |
Improves anger and compulsive and ritualized behavior | Gordon et al., 1993; Sanchez et al., 1996; Hong et al., 2017 | ||
| Anticonvulsants | Lamotrigine | 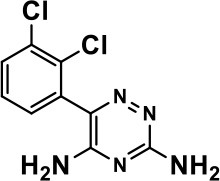 |
Improves overall autistic symptoms | Life-threatening skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, and toxic epidermal necrolysis | Uvebrant and Bauziene, 1994; Jobski et al., 2017 |
| Valproic acid | 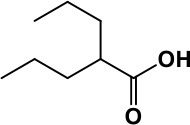 |
Improves receptive language, affective instability, aggression, and social skills | Irritability, weight gain, anxiety | Anagnostou et al., 2006; Hollander et al., 2006, 2010; Jobski et al., 2017 | |
| Levetiracetam | 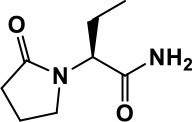 |
Decreases symptoms such as hyperactivity, impulsivity, aggression, and affective lability | CNS effects such as somnolence, decreased energy, headache, dizziness, mood swings and coordination difficulties | Rugino and Samsock, 2002; Jobski et al., 2017 | |
| Glutamate antagonist | Amantadine | 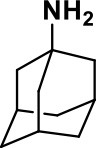 |
Improves hyperactivity and speech disturbance | Nervousness, anxiety, agitation, insomnia, difficulty in concentrating, and exacerbations of pre-existing seizure disorders and psychiatric symptoms in patients with schizophrenia or Parkinson's disease. | King et al., 2001; Naaijen et al., 2017 |
| Memantine | 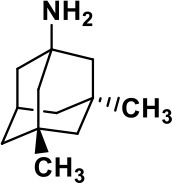 |
Improves memory, hyperactivity, irritability, social behavior and communication, and self-stimulatory behavior | Few autistic individuals experienced worsening of autistic symptoms | Owley et al., 2006; Chez et al., 2007; Naaijen et al., 2017; Vorstman et al., 2017 | |
| Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors | Rivastigmine | 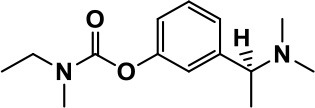 |
Improves overall autistic behavior | Nausea, diarrhea, hyperactivity, and irritability | Vorstman et al., 2017 |
| Donepezil | 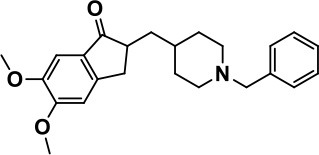 |
Improves irritability and hyperactivity | Nausea and vomiting, decreased appetite and weight loss | Hardan and Handen, 2002; Vorstman et al., 2017 | |
| Galantamine | 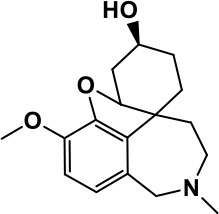 |
Improves several autistic symptoms in children such as irritability, hyperactivity, social interaction deficits, inappropriate speech, loss of attention, and anger | Niederhofer et al., 2002; Nicolson et al., 2006; Vorstman et al., 2017 | ||
| Psycho-stimulant | Methylphenidate | 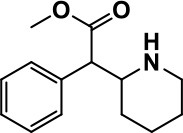 |
Improves several autistic behavioral symptoms in children and adolescents such as hyperactivity, impulsivity, attention, social communication, and self-regulation | Anorexia, aggression, and insomnia | Handen et al., 2000; Di Martino et al., 2004; Jahromi et al., 2009; Kim et al., 2017 |
| Adrenergic α2 receptor agonists | Clonidine | 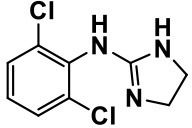 |
Improves hyperactivity, mood fluctuation, aggressiveness and agitation, sleeping pattern and night time awakenings | Sedation, dry mouth, and hypotension | Fankhauser et al., 1992; Ming et al., 2008; Nash and Carter, 2016 |
| Guanfacine | 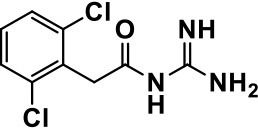 |
Improves attention, hyperactivity, and tics | Insomnia, fatigue, blurred vision, mood instability, sedation, constipation, irritability, and aggression. | Posey et al., 2004; Scahill et al., 2006; Boellner et al., 2007; Nash and Carter, 2016 | |
| Opiate antagonist | Naltrexone | 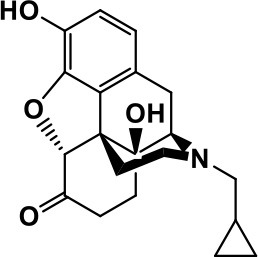 |
Improves, hyperactivity, irritability, self- injuries. However, ineffective in social deficits. | Gastrointestinal complaints such as diarrhea and abdominal cramping. | Panksepp and Lensing, 1991; Bouvard et al., 1995; Kolmen et al., 1995; Elchaar et al., 2006; Clifford et al., 2007; Nash and Carter, 2016 |
Data were obtained from https://clinicaltrials.gov/ last accessed 2017 August 20th.
