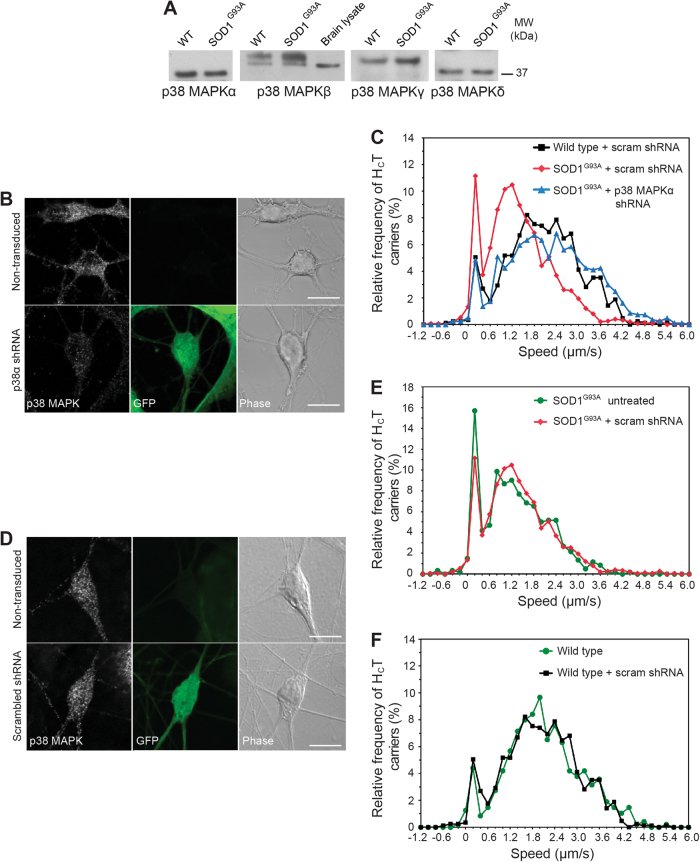
Fig. 4. p38 MAPKα knockdown normalises axonal retrograde transport in SOD1G93A motor neurons.
a Western blot analysis reveals all four p38 MAPK isoforms (α, β, γ and δ) are expressed in wild type and SOD1G93A motor neuron lysates. Mouse brain lysate was loaded as an antibody control for p38 MAPKβ. The upper band is only detected in spinal cord extracts and may represent a posttranslational modified form of p38 MAPKβ. b Lentiviral delivery of shRNA targeted against p38 MAPKα reduces its levels in primary motor neurons. Transduced motor neurons express GFP. c Speed profiles of HCT-containing signalling endosomes in wild-type motor neurons transduced with scrambled shRNA (black squares), SOD1G93A motor neurons transduced with scrambled shRNA (red diamonds) and SOD1G93A motor neurons transduced with p38 MAPKα shRNA (blue triangles). Axonal transport has been quantified only in GFP-positive motor neurons. Comparison of the curves reveals that knocking down p38 MAPKα in SOD1G93A motor neurons (blue triangles) accelerates axonal transport to wild-type speeds (black squares) (wild type + scrambled shRNA: 89 carriers, 17 axons; SOD1G93A + scrambled shRNA: 104 carriers, 24 axons; SOD1G93A + p38 MAPKα shRNA: 99 carriers, 20 axons; 4 independent experiments). d Lentiviral delivery of scrambled shRNA has no effect on levels of p38 MAPKα in primary motor neurons. Transduced motor neurons express GFP. e Speed profiles of HCT carriers in untreated SOD1G93A motor neurons (green circles) and SOD1G93A motor neurons transduced with scrambled shRNA (scram; red diamonds). Comparison of the curves reveals that the scrambled shRNA construct (red diamonds) has no effect on axonal transport speeds (SOD1G93A untreated: 45 carriers, 7 axons; SOD1G93A + scrambled shRNA: 104 carriers, 24 axons; 4 independent experiments). f Speed profiles of HCT carriers in untreated wild-type motor neurons (green circles) and wild-type motor neurons transduced with scrambled shRNA (scram; black squares). Comparison of the curves reveals that scrambled shRNA constructs have no effect on axonal transport speeds (wild-type untreated: 62 carriers, 5 axons; wild type + scrambled shRNA: 89 carriers, 17 axons; 3 independent experiments)