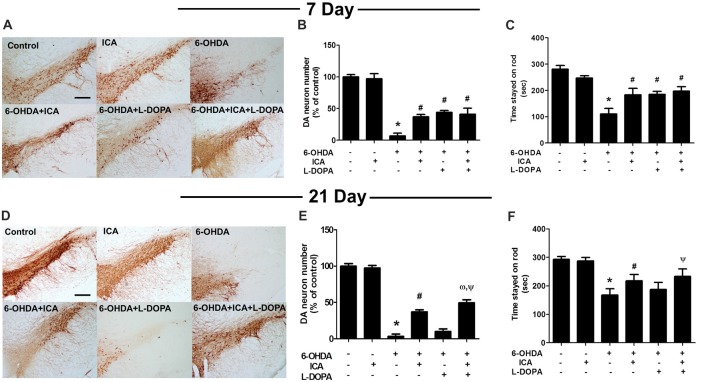
Figure 3.
ICA combined with L-DOPA protected dopamine (DA) neurons from 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in vivo. Rats received unilateral injection of 6-OHDA (8 μg) in the substantia nigra (SN) pars compacts on the left side of the brain. Three weeks later, rats were administrated L-DOPA (25 mg/kg, i.p.) along with ICA (20 mg/kg, p.o.) daily for 3 weeks. After L-DOPA and ICA treatment for 7 and 21 days, rats were sacrificed and SN DA neurons in the brain sections were recognized with an anti-TH antibody (A,D). Scale bar = 200 μm. DA neuronal lesion in the SN was analyzed via the quantification of TH-positive neurons by immunostaining, respectively (B,E). Rat behavior changes were assessed by rotarod test. The time stayed on the rod was recorded (C,F). Data were shown as mean ± SEM from six rats (n = 6). *p < 0.05 compared with the control group; #p < 0.05 compared with 6-OHDA group; ωp < 0.05 compared with 6-OHDA+ICA group; Ψp < 0.05 compared with 6-OHDA+L-DOPA group.