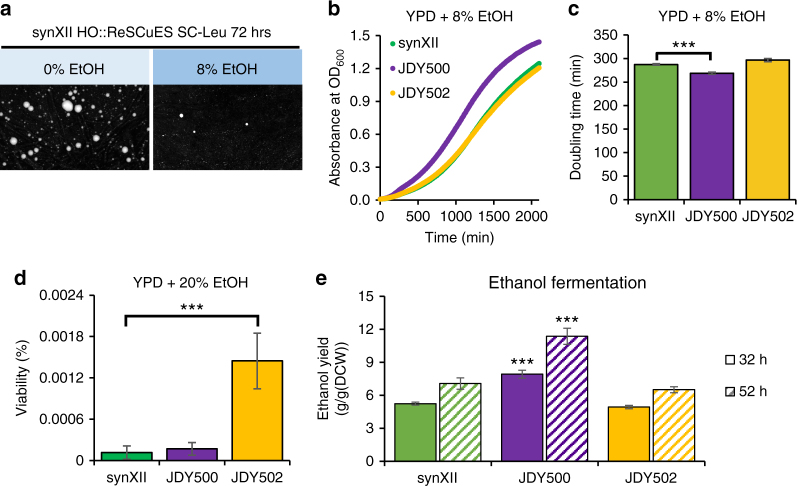
Fig. 3.
Identify the SCRaMbLEd strains with increased ethanol tolerance. a Images of clones on SC-Leu plate with (8%) or without (0%) ethanol. The pictures were taken at 72 h after plating. b Growth curves of two ethanol-tolerant strains (JDY500 and JDY502) in YPD medium with 8% ethanol compared to that of the original synXII strain. The mean of three biological replicates of each strain was shown. c Doubling time (mean ± s.d.) of JDY500 and JDY502 in YPD medium with 8% ethanol compared to that of the original synXII strain. Three biological replicates were measured, *** is for a P-value < 0.01 using two-tailed student t-test. d Viability (mean ± s.d.) of JDY500 and JDY502 compared to that of the original synXII strain after treatment with 20% ethanol for 2 h. Three independent colonies of each strain were tested. *** is for a P-value < 0.01 using two-tailed student t-test. e Measurement of ethanol yields using static fermentation model. The ethanol yield (mean ± s.d.) was measured at 32 and 52 h after switching to the static cultures and presented as gram ethanol per gram dry cell weight (g g−1 (DCW)). Three biological replicates were measured, *** is for a P-value < 0.01 using two-tailed student t-test