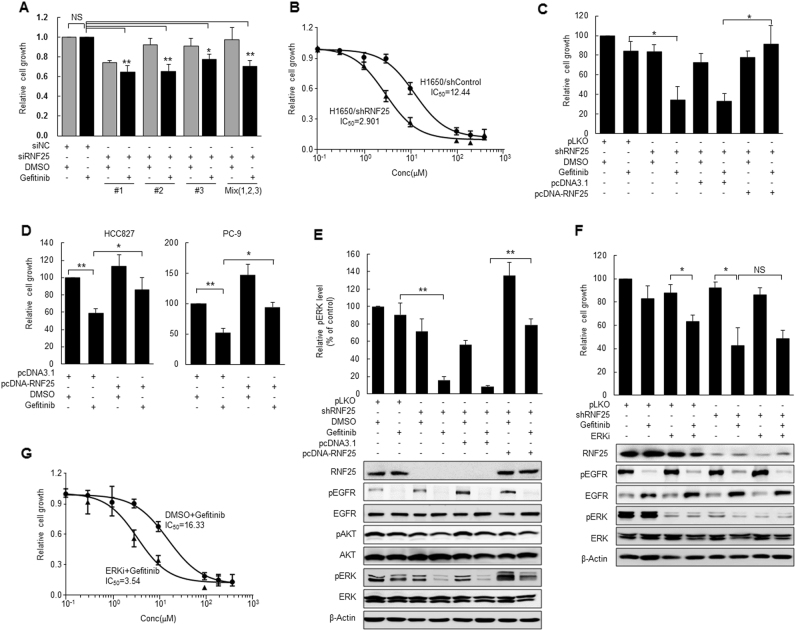
Fig. 2. RNF25 knockdown increases gefitinib sensitivity by inhibiting ERK reactivation in gefitinib-resistant cells.
a H1650 cells were transfected with siRNAs for RNF25 individually or as a mixture, and then treated with gefitinib (5 μM) or DMSO for 72 h. Cell proliferation was measured by cell counting. Values are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. b, c H1650 cells stably transduced with a lentiviral vector carrying shRNF25 (H1650/shRNF25) or pLKO (H1650/shControl) were treated with gefitinib or DMSO for 72 h. The gefitinib sensitivity of each cell line was determined using varying concentrations of gefitinib, and the values are mean ± SD of two independent experiments (b) For reconstitution of RNF25 expression, H1650/shRNF25 (c). d HCC827 or PC-9 cells were transfected with pcDNA-RNF25 or a control vector for 24 h, and then treated with gefitinib (5 μM for H1650, 0.002 μM for HCC827, 0.05 μM for PC-9). For (c, d), values are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. e, f Phosphorylation levels of pro-survival pathway members were analyzed by western blotting in H1650 cells stably transduced with a lentiviral vector carrying shRNF25 or pLKO. The cells were treated with gefitinib (5 μM), ERK inhibitor (ERKi; SCH772984, 10 μM), and/or DMSO for 72 h before the western blot analysis. Values in the bar graphs are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. β-Actin was used as a loading control. g H1650 cells were treated with ERK inhibitor (10 μM) or vehicle in combination with varying concentrations of gefitinib. Values are mean ± SD of two independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by the Student’s t-test (*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01)