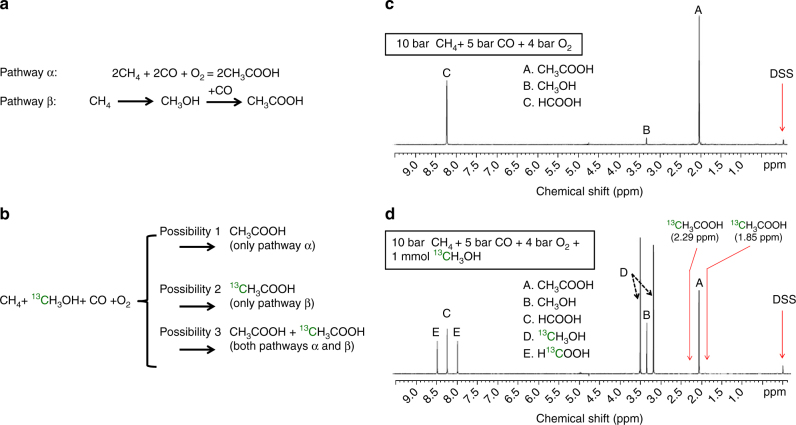
Fig. 5.
Isotope studies for elucidating whether acetic acid could be formed through coupling methanol with CO. a Two potential pathways α and β for production of acetic acid; in pathway α, CH3OH is not an intermediate compound for formation of CH3COOH; in pathway β, CH3OH is an intermediate compound for formation of CH3COOH. b Potential catalytic products formed from 0.10 wt%Rh/ZSM-5 in the mixture of 13CH3OH and H2O in solution under mixture of CH4, CO, and O2 if the transformation of CH4, CO, and O2 follows pathway α, β, or both α and β. c NMR spectra of the products formed from 28 mg of 0.10 wt%Rh/ZSM-5 after reaction in 10 bar CH4, 5 bar CO, and 4 bar O2 at 150 °C for 1 h; there was no any isotope-labeled methanol, 13CH3OH added to the rector before this catalysis test. d NMR spectra of the products formed from 28 mg of 0.10 wt%Rh/ZSM-5 after reaction in 10 bar CH4, 5 bar CO, and 4 bar O2 at 150 °C for 1 h.; notably, 1.0 mmol 13CH3OH was added to H2O before this catalysis test