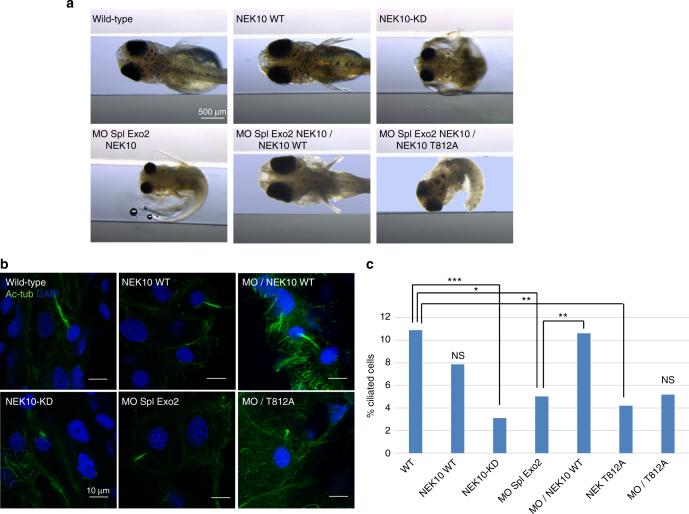
Fig. 5.
NEK10 is required for medaka fish development. a Stereomicroscopic images of WT, NEK10 WT, NEK10-KD, MO-Spl Exo2 Nek10, MO-Spl Exo2 Nek10/NEK10 WT, and MO-Spl Exo2 Nek10/NEK10-T812A injected Medaka larvae, at stage 40. NEK10 WT injected larvae appear morphological identical to control WT larvae. NEK10-KD and MO Spl Exo2 show morphological alterations (i.e., microphthalmia, microcephaly, curved body, and others), which were all reminiscent of defective cilia phenotypes in medaka cilia mutants. NEK10-WT co-injections with MO-Spl Exo2 NEK10 rescued the morphological phenotype that was observed in MO-Spl Exo2 NEK10 larvae. NEK10-T812A co-injections with MO-Spl Exo2 NEK10 were not able to rescue the morphological phenotype observed in MO-Spl Exo2 NEK10 larvae. b Confocal images of cilia of the neural tube cells in the WT, NEK10 WT, MO-Spl Exo2 NEK10/NEK10 WT, NEK10-KD, MO-Spl Exo2 NEK10, MO-Spl Exo2 NEK10/NEK10-T812A stained with anti-acetylated α-tubulin Ab (green) and DAPI (blue). c In the graph is reported cilium length measurements of WT, WT-NEK10, NEK10-KD, MO-Spl Exo2, MO-Spl Exo2/NEK10 WT, NEK10-T812A, and MO-Spl Exo2/NEK10-T812A embryos (n12) (ANOVA test: ***p < 0.000005; **p < 0.00005; *p < 0.0005)