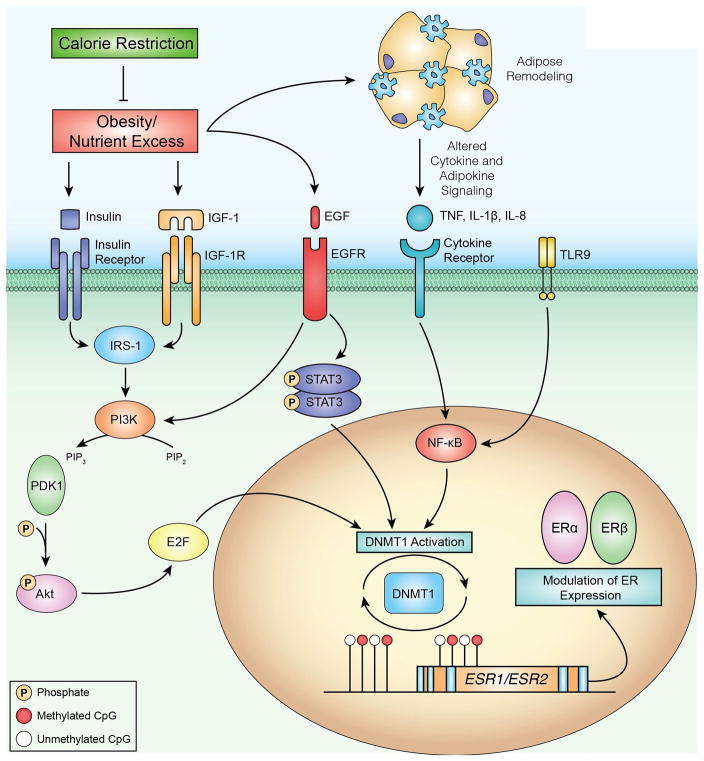
Figure 6.
Proposed model of an energy balance-responsive network associated with DNMT1 regulation, DNA methylation and transcriptional regulation of ERα and ERβ. Obesity and associated energy excess results in several metabolic perturbations that are ameliorated by calorie restriction. To identify regulatory relationships between DNMT1 and other genes that were differentially expressed in our RNA-seq analysis, we used the Path Designer function of Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). We found transcription factors STAT3, NF-kB and E2F to have direct relationships with DNMT1 activation. Upstream of these relationships, IPA also linked growth factors such as insulin and EGF, as well as cytokines including TNF, IL-1β and IL-8, to the E2F, STAT3 and NF-kB signaling pathways. We propose that one consequence of obesity-associated growth factor and cytokine signaling is increased DNMT1 activation, which in turn can modulate DNA methylation and impact transcription of important genes in breast cancer such, as ERα and ERβ. Methylated CpG dinucleotides are indicated by red circles, unmethylated CpG dinucleotides are indicated by white circles.