FIG 1 .
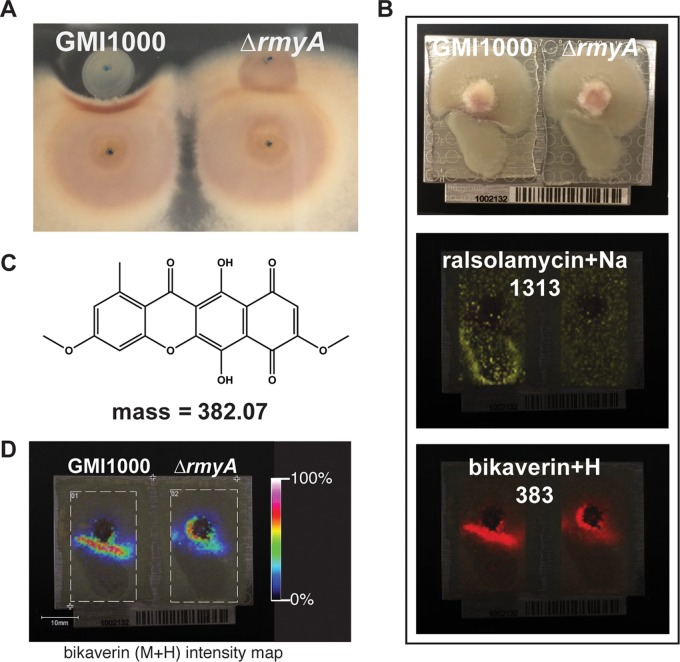
Ralsolamycin induces bikaverin production in F. fujikuroi. (A) When grown in coculture on an agar plate, R. solanacearum GMI1000, but not the ΔrmyA mutant, inhibits growth of F. fujikuroi and induces the production of a red pigment in this fungus. (B) Imaging mass spectrometry experiments. (Top) Picture of cocultures mounted on MALDI plate. (Middle) Ralsolamycin (m/z = 1,313) is the only detectable difference between GMI1000 and ΔrmyA strains. (Bottom) Imaging mass spectrometry shows that bikaverin (m/z = 383) is produced in proximity to bacterial colonies. The complete IMS data set is shown in Fig. S2. (C) Chemical structure of bikaverin and exact mass. (D) Intensity map of bikaverin shows that substantially more compound accumulates proximal to the GMI1000 colony than to the ΔrmyA colony.