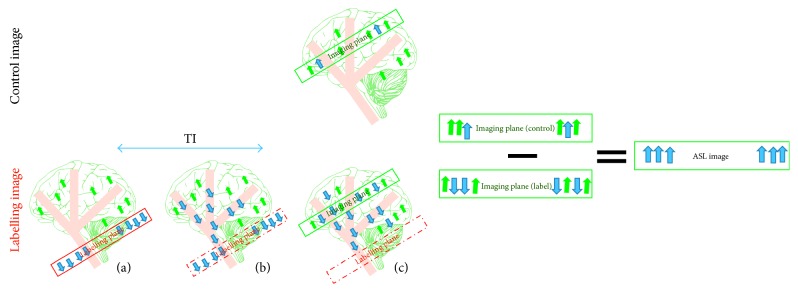
Figure 1.
The drawing shows the main mechanisms of arterial spin labelling (ASL). The labelling image is acquired using blood water as a diffusible tracer. (a) The proximal labelling plane to the imaging target point where the flowing protons are magnetically labelled via inversion (blue arrows); (b) during a delay time, TI, the tagged blood water leaves the label plane and starts to disperse into tissue at the image plane; (c) the labelled image is obtained. The control image is acquired without a labelling pulse in order to extract the tagged blood water from the static tissue (green arrows). Subtracting the two images (control−labelled) leaves the tagged protons, which are directly proportional to the tissue perfusion.