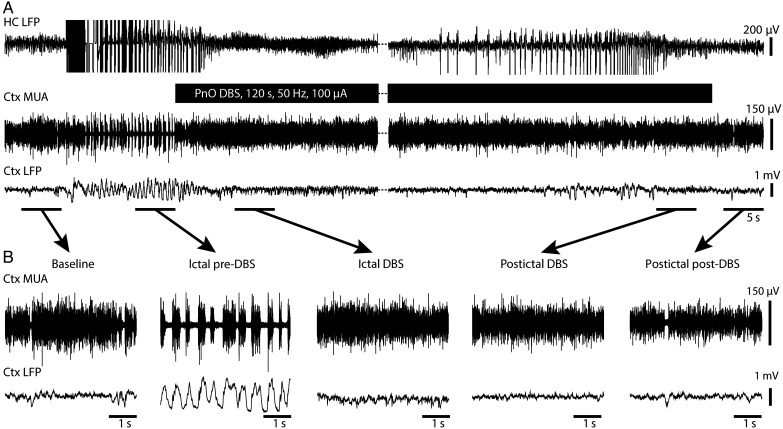
Figure 2.
Cortical physiological arousal with PnO DBS in a focal limbic seizure. (A) Pontine nucleus oralis DBS during focal limbic seizure in a lightly anesthetized animal decreases slowing in lateral orbital frontal cortex. Seizure was induced by 2-s, 60-Hz hippocampal (HC) stimulation. Break in recording of 51 s, during which seizure and DBS continue, enables display of the post-DBS time period. Total DBS duration was 120 s. (B) Five-second-long magnified insets of marked baseline, ictal pre-DBS, ictal DBS, ictal post-DBS, and postictal post-DBS epochs exemplify desynchronized lateral orbital frontal cortical local field potentials (Ctx LFP) intra- and post-DBS. Lateral orbital frontal cortical multiunit activity (MUA) transitions from phasic firing in the ictal pre-DBS period to tonic firing in response to DBS. After PnO stimulation, cortex remains in desynchronized state and no postictal state ensues.