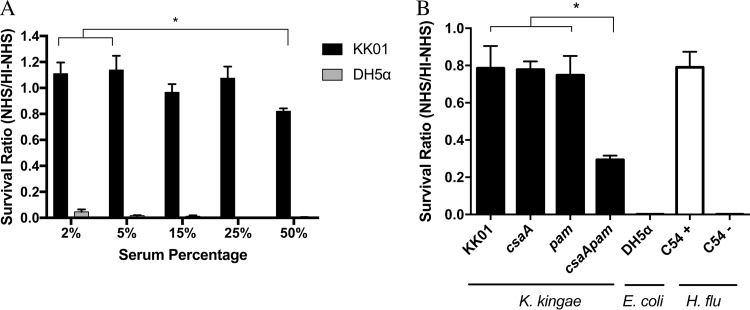
FIG 1.
K. kingae is highly resistant to the bactericidal effects of complement present in pooled normal human serum, and elimination of both surface polysaccharides decreases serum resistance in K. kingae. (A) K. kingae strain KK01 and E. coli strain DH5α (∼103 CFU) were incubated with 2%, 5%, 15%, 25%, or 50% NHS or HI-NHS for 1 h. (B) K. kingae strains KK01, KK01 csaA, KK01 pam, and KK01 csaA pam, E. coli strain DH5α, and H. influenzae (H. flu) strains C54+ (encapsulated) and C54− (nonencapsulated) were incubated with 50% NHS or 50% HI-NHS for 1 h. The survival ratio was calculated by dividing the NHS CFU counts by the HI-NHS CFU counts. Abbreviations: csaA, KK01 csaA; pam, KK01 pam; csaApam, KK01 csaA pam. A total of three biological replicates were performed (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined with an unpaired Student's t test, and the error bars represent the standard error of the mean. *, P < 0.05.