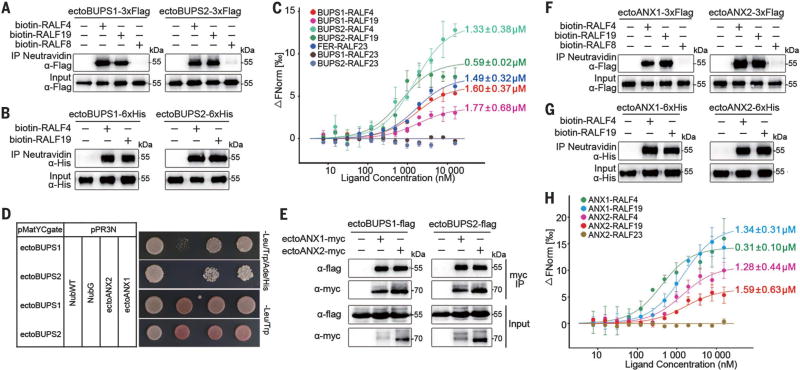
Fig. 3. BUPS1/2, ANX1/2, and RALF4/19 interact with each other.
(A) Pull-down assay between Flag-tagged ectodomains of BUPS1/2 (purified from tobacco leaves) and biotinylated RALF4/19. (B) Pull-down assay between insect cell–expressed His-tagged ectodomains of BUPS1/2 and biotinylated RALF4/19. (C) Binding affinity between BUPS1/2 and RALF4/19 by MST analysis; Kd values are as indicated. The published RALF23-FER Kd value is 0.31 µM (24). ΔFNorm, change in fluorescence. (D) Dual-membrane yeast two-hybrid assays of BUPS1/2 and ANX1/2. (E) Interaction of BUPS1/2 and ANX1/2 through their ectodomains, as assessed by coimmunoprecipitation assay. The ectodomains of BUPS1/2 and ANX1/2 were coexpressed in tobacco leaf cells. (F and G) ANX1/2-Flag (F) and ANX1/2-His (G) interact with biotinylated RALF4/19 by pull-down assays. (H) MST analysis of the binding affinity between ANX1/2 ectodomains and RALF4/19. Error bars in (C) and (H) are SEM of two independent experiments.