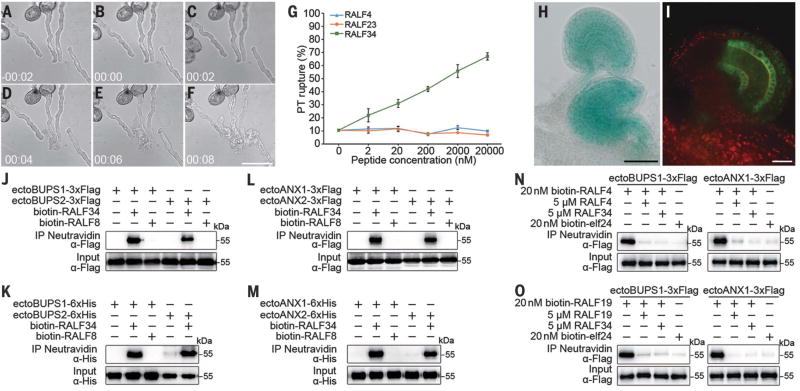
Fig. 4. RALF34 triggers pollen tube burst and interacts with and competes for the ANX-BUPS receptor complex.
(A to F) Time-course imaging of pollen tube discharge induced by RALF34 treatment; 20 µM peptide was used to test the effect on growing wild-type pollen tubes. The pollen tube discharge occurs less than 10 s after RALF34 treatment. (G) Quantitative analysis of pollen tube rupture treated with different concentrations of RALF4, RALF23, and RALF34. Data are means ± SD (n = 230 pollen tubes of each treatment for two independent experiments). (H) RALF34p::GUS expressed predominantly in mature ovules. (I) RALF34-GFP protein expressed in ovules. (J to M) Pull-down assays between biotinylated RALF8/34 and Flag- or His-tagged ectodomains of BUPS1/2 [(J) and (K)] or between biotinylated RALF8/34 and Flag- or His-tagged ectodomains of ANX1/2 [(L) and (M)]. (N and O) RALF34 peptide outcompetes biotinylated RALF4/19 interaction with Flag-tagged ectodomain of BUPS1 or ANX1. Scale bars, 50 µm [(A) to (F), (H)], 20 µm (I).