Fig. 1.
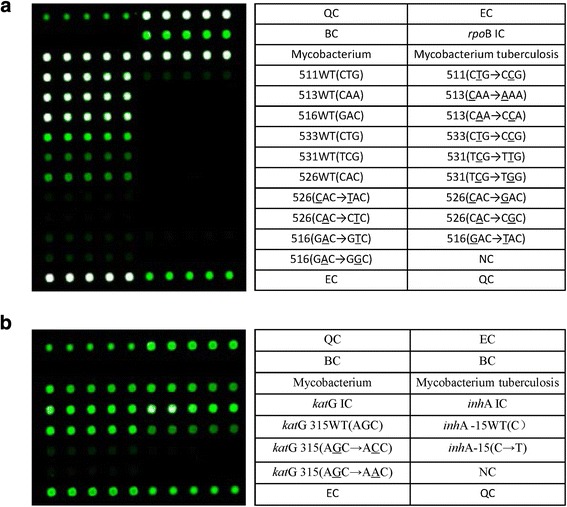
CapitalBio™ DNA microarray detection site layout. The contents of the table on the right side correspond to the microarray hybridization dot matrix on the left side in each figure. Every five repeated hybrid grid points correspond to one cell of specific content. QC: surface chemical quality control probe; EC: external control probe for hybridization-based quantitation; BC: blank control; NC: negative control probe; IC: internal control probe for PCR; WT: wild-type. a: Six sites detected in the rpoB gene, Ser531Leu (TCG → TTG), Ser531Trp (TCG → TGG), His526Asp (CAC → GAC), His526Tyr (CAC → TAC), His526Leu (CAC → CTC), His526Arg (CAC → CGC), Leu511Pro (CTG → CCG), Gln513Leu (CAA → CCA), Gln513Lys (CAA → AAA), Asp516Val (GAC → GTC), Asp516Tyr (GAC → TAC), Asp516Gly (GAC → GGC) and Leu533Pro (CTG → CCG), for a total of 13 types of mutants. b: The katG gene and a locus of the inhA gene promoter were tested as isoniazid resistance-related genes. The contents of the table on the right side correspond to the microarray hybridization dot matrix on the left side in each figure. Two katG gene mutants, Ser315Thr (AGC → ACC) and Ser315Asn (AGC → AAC), and one inhA gene promoter mutant, − 15 (C → T) mutant, were identified
