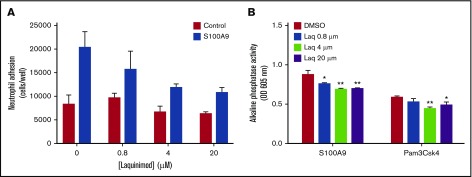
Figure 2.
The quinoline-3-carboxamide laquinimod partially inhibits neutrophil adhesion and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation in THP-blue cells stimulated with S100A9. (A) Neutrophils were labeled with calcein acetoxymethyl ester and preincubated with increasing concentrations of laquinimod or its diluent (DMSO) for 30 minutes. Cells were then added to fibrinogen-coated 96-well plates, and adhesion was allowed for 30 minutes in the presence or absence of S100A9 (10 µg/mL). After washings, adherent cells were lysed by adding deionized distilled water, and fluorescence was measured at λex = 485 nm and λem = 530 nm using a 96-well plate fluorescence reader. The number of neutrophils per well was determined using a standard curve of serially diluted calcein-AM-labeled neutrophils. Data are from 1 experiment representative of 4, with error bars (± SEM) for the 3 replicates. (B) Cells of the monocyte line THP-blue, which stably expresses an NF-κB/activator protein 1–inducible secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase gene construct, were preincubated for 30 minutes with increasing concentrations of laquinimod (Laq) or with its diluent (DMSO). The cells were then stimulated for 20 hours with 10 µg/mL of S100A9 or 1 µg/mL of Pam3Csk4. Alkaline phosphatase activity secreted into the culture supernatant was then measured using Quanti-Blue according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Fisher Scientific, Ottawa, ON, Canada). Data shown are the optical density at 605 nm measured in 1 experiment representative of 3, with error bars (± SEM) for the 3 replicates (*P ≤ .05; **P ≤ .01; based on Dunnett’s multiple comparison test). OD, optical density.