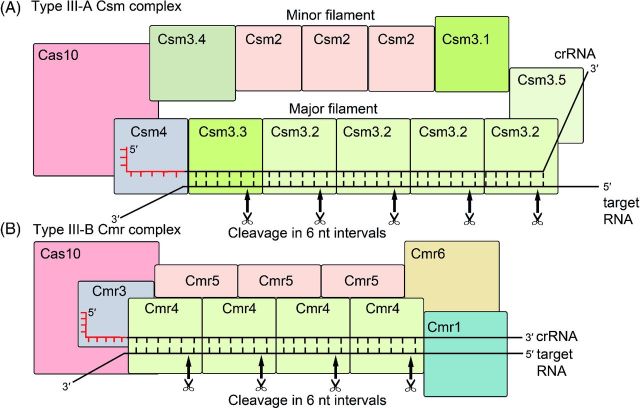
Figure 7.
Comparison of type III crRNP-mediated RNA interference. (A) The type III-A Csm complex of Su. solfataricus is composed of 13 subunits that are arranged as a basal body and two intertwined filaments. Located at the base of the Csm complex is the large subunit Cas10, serving as an anchor for the major and the minor filament. The major filament consists of Csm4 and six Csm3 subunits and binds the crRNA. The minor filament consists of three Csm2 subunits and two additional Csm3 subunits. The Csm3 units that form the backbone of the Csm complex were shown to act as target RNA nucleases (indicated by a scissor) in S. thermophilus. (B) The type III-B Cmr complex of P. furiosus contains an extended helical backbone composed of Cmr4 and Cmr5 subunits. The tail is composed of the stable heterodimer Cas10 and Cmr3, while the curled head contains Cmr1 and Cmr6. The crRNA-binding backbone is formed by several Cmr4 subunits, while the Cas10-Cmr3 heterodimer plays a role in the recognition of the crRNA 5′ handle. A second helical structure is formed by three Cmr5 subunits and is inserted alongside the helical Cmr4 filament. Cleavage of target RNA by Cmr4 was observed in 6-nt intervals (indicated by a scissor).