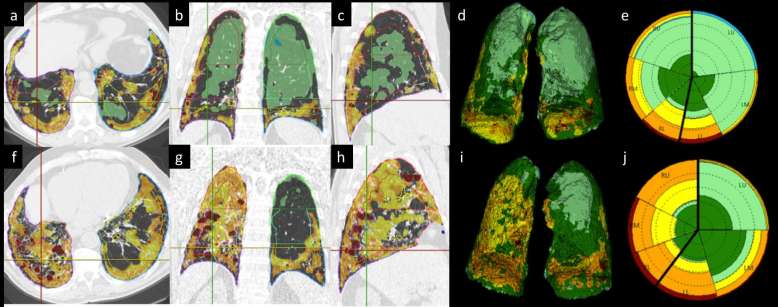
Figure 6. .
(a–j) Longitudinal quantitative analysis of fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Automatic volumetric segmentation of parenchymal abnormalities in a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis at baseline (top row: a−e) and 1-year follow-up (bottom row: f−j). The colour-coded overlay on native high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) images shows the distribution of parenchymal abnormalities on axial, coronal and sagittal reconstruction at baseline (a−c) and 1 year (f−h). The data are also provided in a volumetric model that shows both lungs with colour-coded characterization of parenchyma volume. Furthermore, a synthetic 2D graph (the so-called Glyph) is built that provides comprehensive display of abnormal parenchyma and its distribution between lobes (baseline Glyph in e, 1-year Glyph in j). 2D, two-dimensional.