Figure 3. Crosstalk between two nutrient-sensing pathways.
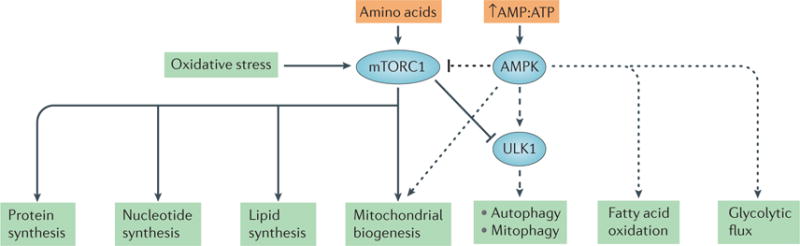
Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) have key roles in regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy. mTORC1 is responsible for triggering anabolic pathways, such as the synthesis of proteins, nucleotides and lipids, as well as mitochondrial biogenesis. AMPK activates catabolic pathways, including autophagy, mitophagy, fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis. AMPK can stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis (dotted arrow). However, in response to stimuli such as nutrient deprivation, AMPK can inhibit mTORC1 (dotted inhibitory line) and phosphorylate ULK1 to activate mitophagy (dashed arrow). Together these two signalling pathways maintain cell function and sustain mitochondrial energetics in response to stimuli such as hypoxia, oxidative stress and energy depletion.
