Figure 4. Activation and regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis.
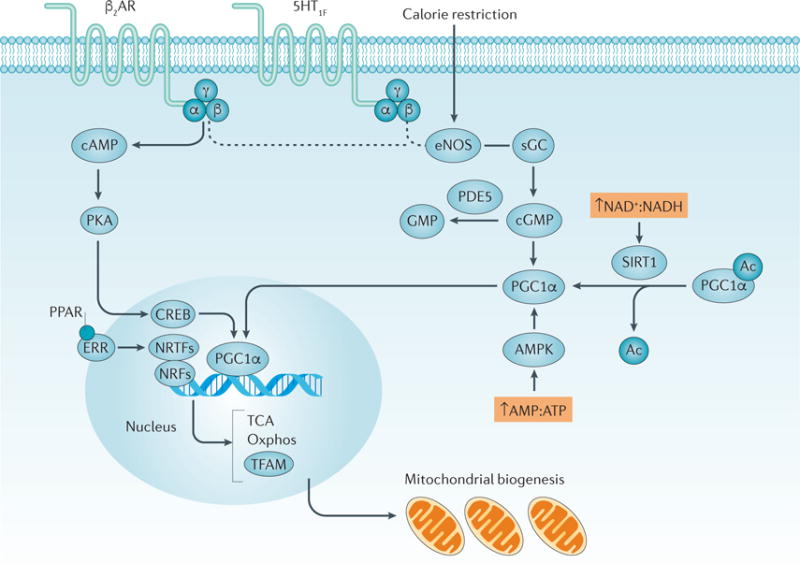
A complex network of pathways regulate mitochondrial biogenesis. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator 1α (PGC1α) in the cytosol causes its translocation to the nucleus and the transcription of genes (including that encoding mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and mitochondrial biogenesis. TFAM aids in the transcription of genes that are encoded by mitochondrial DNA224–226. The activation of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), such as the β2 adrenergic receptors (β2AR) and 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1F (5-HT1F), leads to the dissociation of heterotrimeric G proteins composed of Gα, Gβ and Gγ subunits and the subsequent activation of protein kinase A and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)66. The pathway from GPCRs to eNOS is still under investigation, as indicated by the dashed line. eNOS stimulates soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) to form cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which in turn activates PGC1α. A number of compounds can activate nuclear receptors such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and oestrogen- related receptors (ERRs) and induce mitochondrial biogenesis. Once activated, these nuclear receptors can act as transcriptional co-activators (labelled in the figure as nuclear receptor transcription factors (NRTFs)), with PGC1α to stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis. Other transcription factors, including nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1) and NRF2, can also directly bind to PGC1α to induce mitochondrial biogenesis227. Stimuli, such as caloric restriction, can activate eNOS, increasing the production of cGMP and leading to the activation of PGC1α. The activity of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) is increased in the presence of a high ratio of NAD+ to NADH concentrations, leading to the activation of PGC1α. High AMP:ATP ratios also activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), activating PGC1α by phosphorylation. In all of these cases, the activation of PGC1α stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis. Ac, acetyl; PDE5, cGMP-specific 3ʹ,5ʹ-cyclic phosphodiesterase; PKA, protein kinase A; sGC, soluble guanylyl cyclase.
