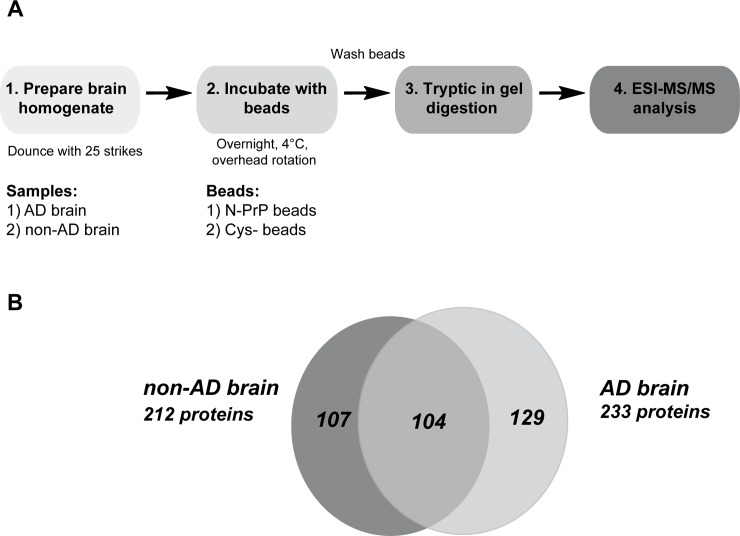
Fig 2. Characterization of N-PrP-interacting proteins.
A. Schematic representation of the experimental approach. Parietal cortex samples of a non-AD and an AD brain were dissolved in lysis buffer (25% w/v) homogenized with 25 strikes in a glass douncer, and centrifuged (7,500 x g, 4°C). The supernatant was added to the PrP23-114 beads and incubated overnight at 4°C. As a control, lysates were incubated with cysteine-modified beads. To purify interaction partners, beads were washed extensively in lysis buffer. Finally, beads were pelleted by centrifugation and boiled in SDS buffer. The SDS-soluble fraction was separated by SDS-PAGE and proteins co-purified with the beads were identified by ESI-MS/MS after tryptic in-gel digestion. B. Venn diagram of proteins interacting with PrP23-114 in non-AD and AD brain. The overlap represents PrP23-114-interacting proteins identified in both brain samples.