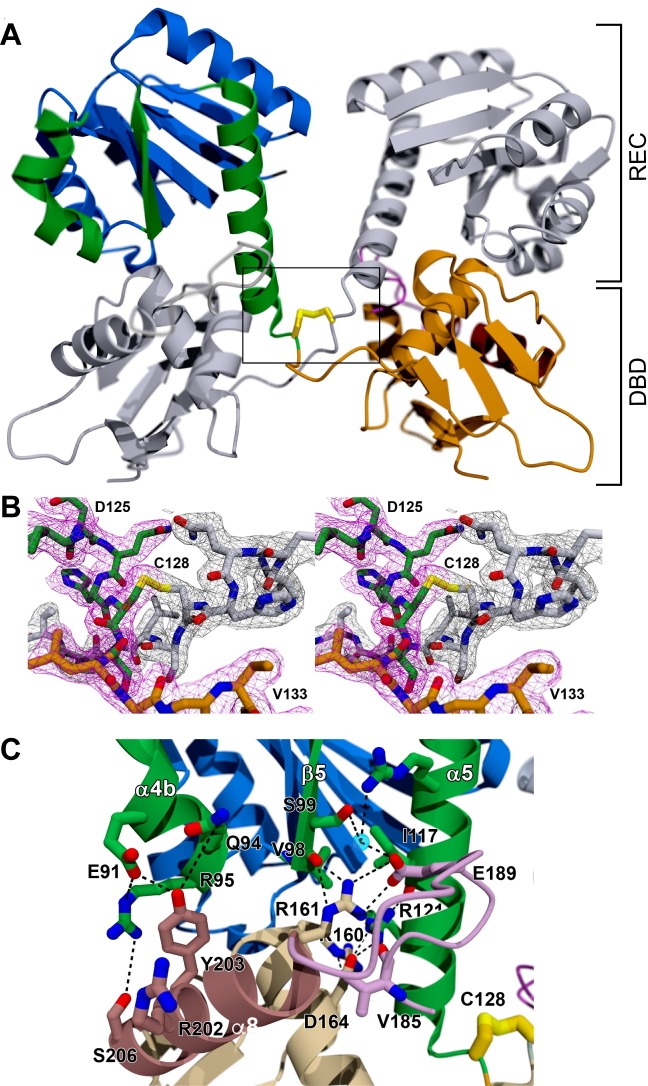
Fig 4. RitR oxidized structure.
(A) Cartoon representation of the domain-swapped RitROX structure. One protomer is in color and the other protomer in grey. REC, receiver domain; DBD, DNA-binding domain. (B) 2|Fo|-|Fc| composite omit electron density for the inter-protomer Cys128:Cys128’ disulfide bond and surrounding residues that pins the C-terminal ends of each α5 helix together. As a consueqence, both DBDs are in close proximity. One protomer is shown in color with a pink density map, and the other protomer is shown in grey with a matching grey density map. (C) Image of the interface between the DBD of one protomer of the RitROX homodimer (bright colors) and the REC domain of the other protomer (muted colors). The interactions are almost identical to those observed for the C128S structure in Fig 3C.