Figure 9.
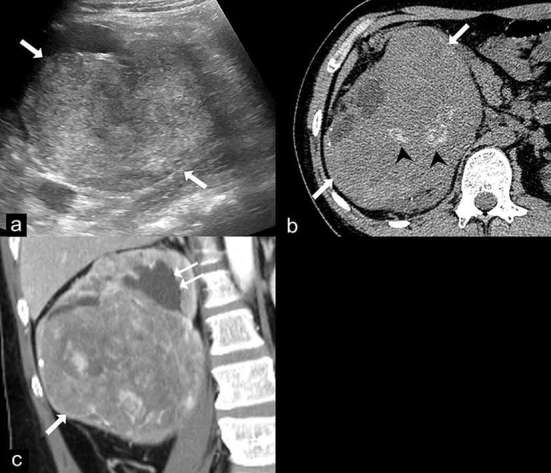
Epithelioid angiomyolipoma (EAML). Ultrasound (a) demonstrates a large heterogeneous hyperechoic mass in the right kidney (arrows). Axial unenhanced CT image (b) shows a 14 cm renal mass (arrows) with internal calcifications (arrow heads) and no gross fat component. Coronal contrast-enhanced CT image (c) shows the heterogeneous enhancing mass (arrow) in the lower pole of the right kidney which compresses the renal pelvis, causing mild dilatation of the upper pole calyces (double arrows). Renal cell carcinoma was suspected and a radical nephrectomy was performed. The final diagnosis of EAML was proven by histopathology and immunohistochemistry.
