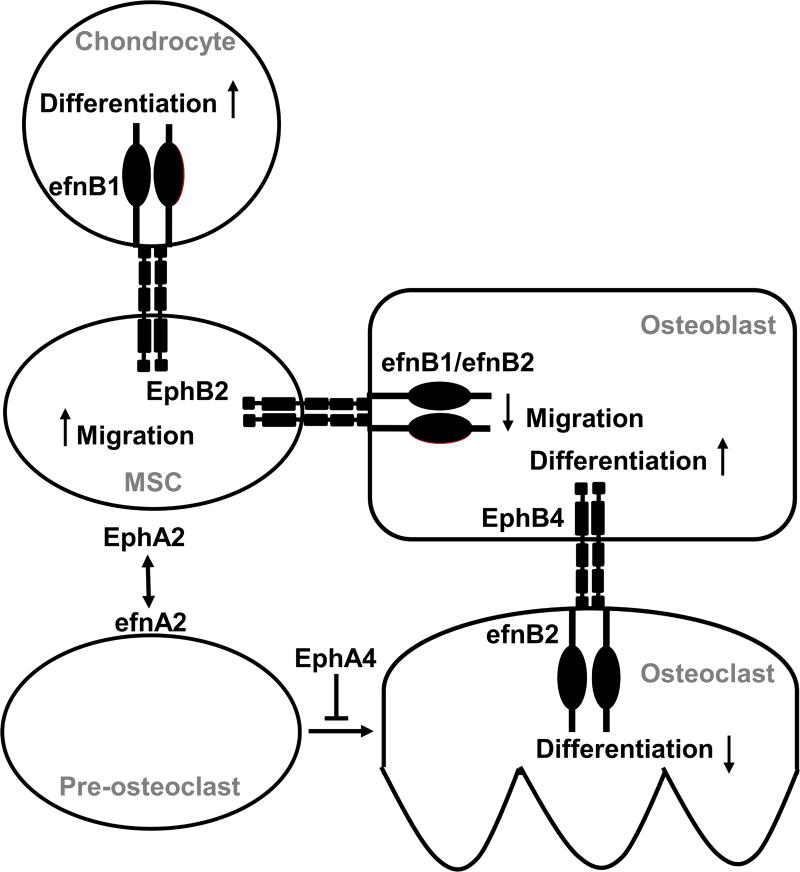
Figure 2. A model for efn–Eph regulation of bone cell interaction in bone development and homeostasis.
Several efns and Ephs mediate growth plate development during bone growth. Interactions between osteoblasts (OB), osteoclasts (OC), mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), and chondrocytes are mediated by different ligand–receptor combinations, coordinating bone cell development and activity through forward and reverse signaling. Osteoblast development is mediated by forward signaling through EphB4 from efnB2 (Zhao et al. 2006) and reverse signaling through efnB1/efnB2 from EphB2 (Arthur et al. 2011). Osteoclast development is mediated by efnA2 and EphA4 (Irie et al. 2009; Liu et al. 2017) as well as through reverse signaling from EphB4 through efnB2 (Zhao et al. 2006).